Methods for Access Control
Question
John is a software contractor and is working on a web application.
Since the budget is limited and the schedule is tight, he decides to implement it using API gateway and Lambda so that he does not need to consider the server management, scalability, etc.
The customer has raised concerns that the APIs should be kept secure and there should be mechanisms to control the access to API endpoints.
Which below method can be used to help secure the API?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D. E.Correct Answer - E.
Multiple mechanisms can be used to control access to the API in the API gateway.
And several methods can be used together to implement a very granular and secure application.
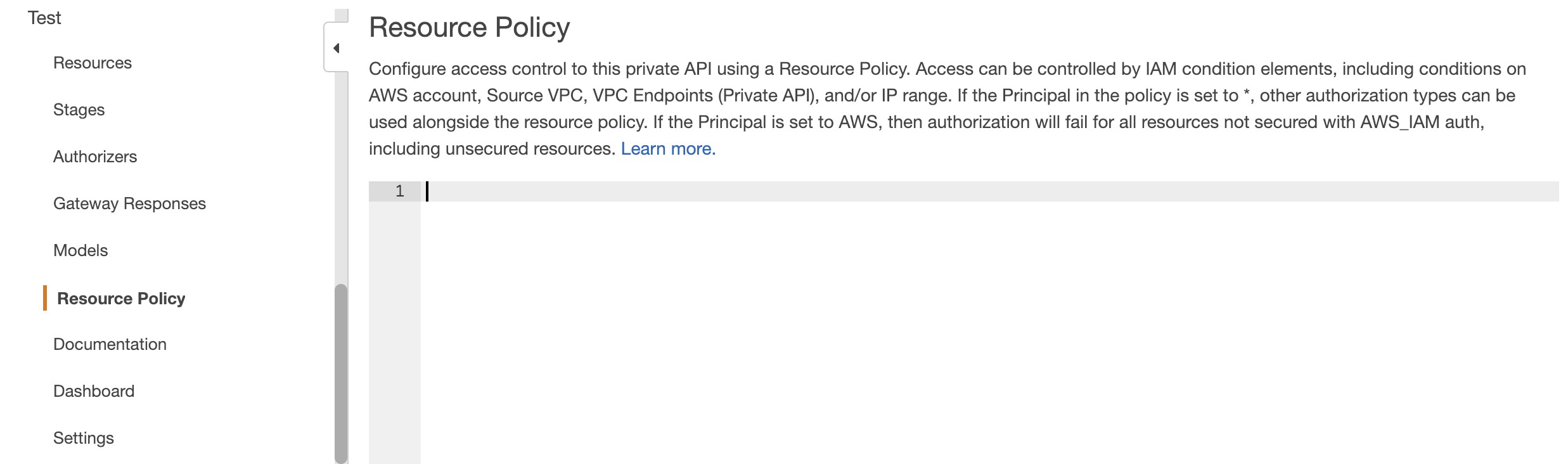
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/apigateway-control-access-to-api.htmlThe below mechanisms can be chosen.
Resource policies let you create resource-based policies to allow or deny access to your APIs and methods from the specified source IP addresses or VPC endpoints.
It can be configured in the API Gateway console:
Standard AWS IAM roles and policies offer flexible and robust access controls that can be applied to an entire API or individual methods.
The below is an IAM policy example of calling the Lambda function:
Lambda authorizers are Lambda functions that control access to REST API methods using bearer token authentication and information described by headers, paths, query strings, stage variables, or context variables request parameters.
In the API Gateway console, lambda authorizers can be created in the below place.
Amazon Cognito user pools let you create customizable authentication and authorization solutions for your REST APIs.
As a result, option E is correct.
Sure, I'd be happy to explain the answer to this question in detail!
To recap, John is developing a web application using API Gateway and Lambda, and the customer is concerned about security and controlling access to API endpoints. The question asks which method can be used to help secure the API, and provides five possible answers. Let's go through each option and explain what it entails.
A. Attach a resource policy to the API Gateway API, which controls access to the API Gateway resources. Access can be controlled by IAM condition elements, including conditions on AWS account, source VPC, etc.
This answer suggests using a resource policy to control access to the API Gateway API. A resource policy is a JSON document that specifies who has access to the API Gateway resources, and what actions they can perform. It can be used to control access based on a variety of conditions, including the AWS account making the request, the IP address of the client, the HTTP method being used, and more. Resource policies can be attached to API Gateway APIs, stages, and methods, and can be used to grant or deny access.
In this case, the answer suggests using IAM condition elements to control access. IAM condition elements allow you to specify additional conditions that must be met before a request is allowed. For example, you could require that the request come from a specific IP address range, or that the request includes a certain header or query string parameter. By using IAM condition elements in conjunction with a resource policy, you can create very granular access control rules.
B. Use IAM permissions to control access to the API Gateway component. For example, in order to call a deployed API, the API caller must be granted permission to perform required IAM actions supported by the API execution component of API Gateway.
This answer suggests using IAM permissions to control access to the API Gateway component. IAM permissions are used to control access to AWS resources, including API Gateway. By default, IAM users do not have access to API Gateway, so you will need to grant them permissions in order to use it.
To control access to API Gateway using IAM permissions, you can create an IAM policy that grants or denies access to specific API Gateway resources. For example, you could create a policy that allows a user to call a specific API, but not to create or delete APIs. IAM policies can be very granular, allowing you to specify exactly what actions a user is allowed to perform on a given resource.
C. Use a Lambda function as the authorizer. When a client calls the API, the API Gateway either supplies the authorization token that is extracted from a specified request header for the token-based authorizer or it passes in the incoming request parameters as the input to the request parameters-based authorizer Lambda function.
This answer suggests using a Lambda function as the authorizer for the API. An authorizer is a Lambda function that authenticates and authorizes incoming API requests. When a client makes a request to the API, the authorizer function is invoked to determine whether the client is allowed to access the requested resource.
There are two types of authorizers in API Gateway: token-based and request parameter-based. Token-based authorizers extract a token from a specified header in the request and pass it to the authorizer function, while request parameter-based authorizers pass the entire request to the function. The authorizer function then returns an IAM policy document that specifies whether the client is authorized to access the requested resource.
Using a Lambda function as an authorizer allows you to implement custom authentication and authorization logic. For example, you could use a Lambda function to authenticate users against a database, or to check whether they have the necessary permissions to access a resource.
D. Use an Amazon Cognito user pool to control who can access the API in Amazon API Gateway. You need to use the Amazon
