Rectifying Slow Response Times for NAT Instance
Question
Your team is using a NAT instance on an Linux EC2 Instance.
The private subnet has a route added for 0.0.0.0/0 for the NAT instance.
This NAT instance is being used to download updates from the Internet for instances in the private subnet.
But the IT administrators who are in charge of applying the updates complain of slow response times.
What can be done to rectify this issue? Choose 2 answers from the options given below.
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - B and C.
The bandwidth capability of the NAT instance depends on the Instance type.
Below is a part of the comparison of NAT instances and NAT gateways from the AWS Documentation.
So one option is to replace the NAT instance with a NAT gateway.
The other option is to upgrade the instance type of the current NAT instance.
Option A is incorrect because this is not possible to add 2 routes for the same destination.
Option D is incorrect because the NAT instance has to be in a public subnet.
For more information on the comparison of NAT instances with NAT gateways,please refer to the below link.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonVPC/latest/UserGuide/vpc-nat-comparison.html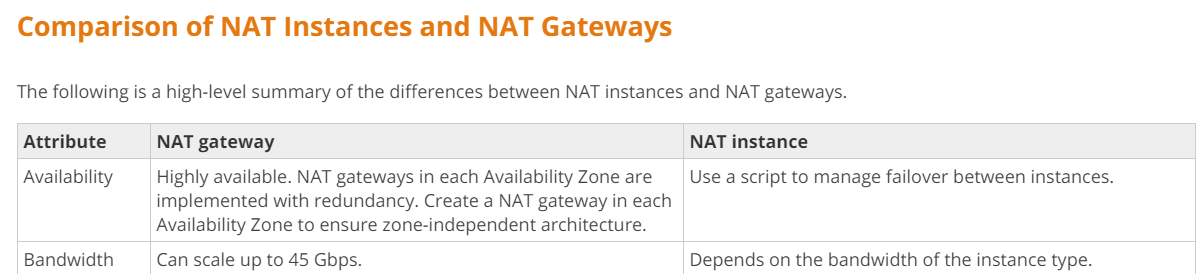
The issue is that the IT administrators are experiencing slow response times when applying updates to instances in the private subnet, which are routed through a NAT instance. To address this issue, we need to improve the performance of the NAT instance.
Option A: Adding Another NAT Instance: Adding another NAT instance and routing traffic to both instances will provide redundancy and load balancing. This will improve the availability and performance of the NAT service, as requests will be distributed across multiple instances. Therefore, this option is a valid choice.
Option B: Replacing the NAT Instance with a NAT Gateway: A NAT Gateway is a fully managed NAT service provided by AWS. It automatically scales up or down to meet the demand of your applications, and does not require you to manage the underlying infrastructure. A NAT Gateway is recommended when you need to support high levels of traffic, and it is also recommended when you need to adhere to strict compliance requirements, such as PCI DSS. Therefore, replacing the NAT instance with a NAT Gateway is a valid and better option than adding another NAT instance.
Option C: Upgrading the NAT Instance to a Larger Instance Type: Upgrading the instance type can improve the performance of the NAT instance by providing more CPU, memory and network resources. However, it is important to note that this solution may not be as effective as the other options, as the performance of the NAT instance is limited by the network bandwidth and not just the resources of the instance itself.
Option D: Moving the NAT Instance to the Private Subnet: Moving the NAT instance to the private subnet will not solve the issue, but instead, it will worsen it. As the traffic from the private subnet needs to go through the NAT instance to reach the internet, moving the NAT instance to the private subnet will increase the latency, which will further decrease the performance.
Therefore, the two best options to improve the performance of the NAT instance are:
- Replacing the NAT instance with a NAT Gateway
- Adding another NAT instance and routing traffic to both instances.