Ensure Patching and Up-to-Date EC2 Instances in Private Subnet
Question
You have a set of 100 EC2 Instances in an AWS account.
You need to ensure that all of these instances are patched and kept to date.
All of the instances are in a private subnet.
How can you achieve this? Choose 2 answers from the options given below.
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A and B.
Option C is incorrect because SSH port 22 is not required for the SSM Patch Manager to work with EC2 instances.
Option D is incorrect because the AWS inspector can only detect the patches.
One of the AWS Blogs mentions how patching of Linux servers can be accomplished.
Below is the diagram representation of the architecture setup.
For more information on patching Linux workloads in AWS, please refer to the link:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/how-to-patch-linux-workloads-on-aws/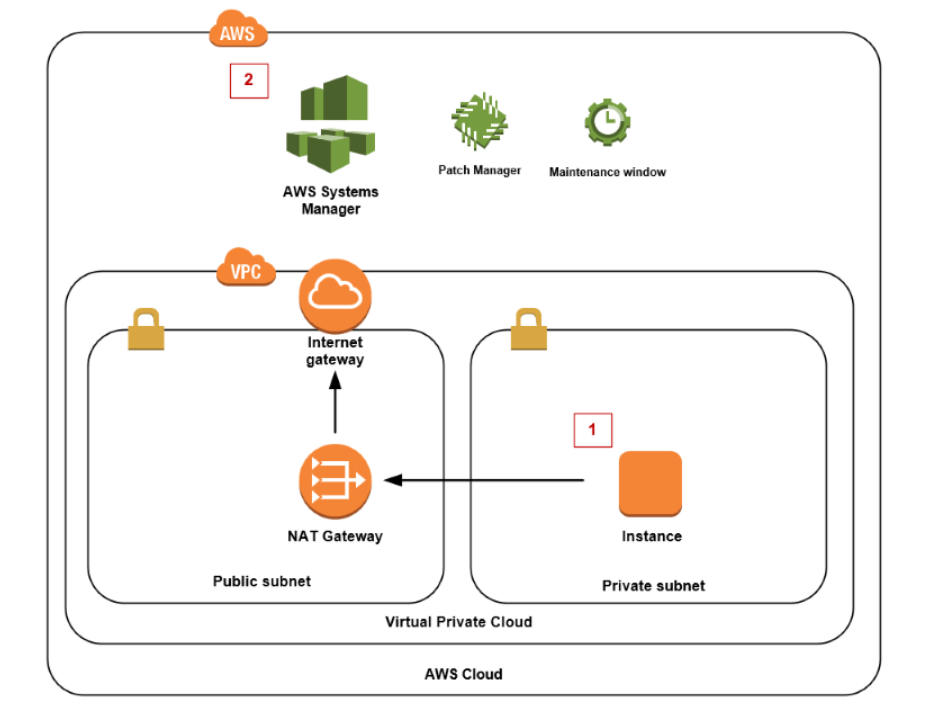
To ensure that all of the 100 EC2 instances are patched and kept up-to-date, we need to use a combination of two methods. The two methods that can be used are:
B. Use the Systems Manager to patch the instances.
AWS Systems Manager is a management service that helps in automating administrative tasks for AWS resources. With Systems Manager, we can easily manage EC2 instances that are in private subnets. Systems Manager Patch Manager automates the process of patching Amazon EC2 instances running Linux or Windows. We can use Patch Manager to patch both Amazon EC2 instances in public and private subnets, and on-premises instances. By using this service, we can schedule patching and automate the process of patching.
To use Systems Manager Patch Manager, we need to create a patch baseline. A patch baseline defines the operating system patches and other updates that should be applied to instances. We can then use this patch baseline to create a patching schedule, which we can use to automate the patching process.
D. Use the AWS Inspector to patch the updates.
Amazon Inspector is an automated security assessment service that helps in improving the security and compliance of applications deployed on AWS. It helps in identifying security vulnerabilities in the applications and infrastructure deployed on AWS. Inspector can be used to identify common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs) in EC2 instances.
To use Amazon Inspector, we need to create an assessment template. An assessment template is a set of rules that Inspector uses to evaluate the security of the target resource. We can create an assessment template for EC2 instances and configure the rules to check for vulnerabilities and exposures. Inspector generates a report that lists the vulnerabilities and exposures found in the instances. We can then use this report to patch the instances.
To summarize, we can use Systems Manager Patch Manager to automate the patching process for EC2 instances in private subnets, and we can use Amazon Inspector to identify vulnerabilities and exposures in the instances. By using these two services together, we can ensure that all of the instances are patched and kept up-to-date.
