Selecting the Right Storage for High-Performance MongoDB Hosting
Question
A company wants to host a selection of MongoDB instances.
They are expecting a high load and want to achieve high performance.
As an architect, you need to ensure that the right storage is used to host the MongoDB database.
Which of the following would you incorporate as the underlying storage layer?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A.
The below snapshot from the AWS Documentation shows the different volume types and why Provisioned IOPS is the most ideal for this requirement.
Also, Provisioned IOPS is recommended for NoSQL and Relational Databases.
Because of what is mentioned in the documentation as the ideal storage type, the other options are invalid.
For more information on the different EBS volume types, please visit the below URL-
https://aws.amazon.com/ebs/details/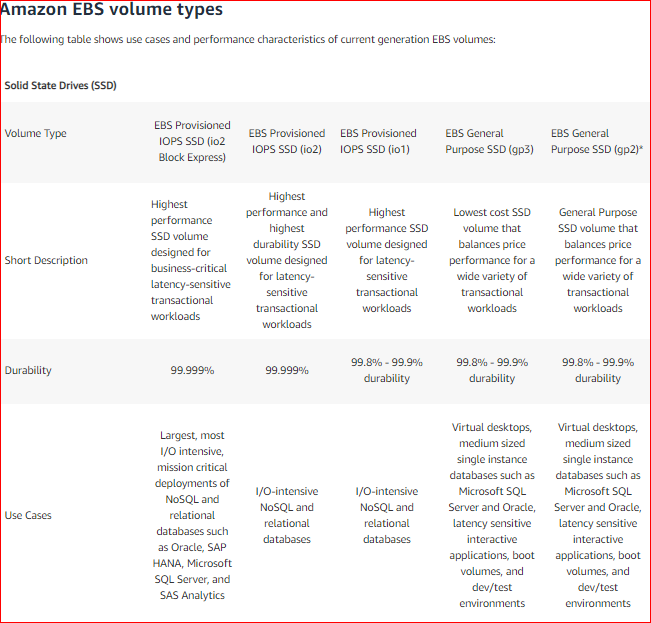
When selecting storage for a MongoDB instance, it is essential to consider the expected workload, the type of operations, and the performance requirements. Here are the explanations of the storage options listed in the question and their suitability for hosting MongoDB databases:
A. Provisioned IOPS SSD (Solid State Drive): This storage option offers consistent high-performance I/O operations per second (IOPS) with low latency. Provisioned IOPS SSD is recommended for high-performance applications that require low latency and high throughput for both read and write operations, such as large-scale MongoDB deployments with a high number of transactions per second (TPS). It provides the necessary level of IOPS required to support write-heavy workloads and provides the necessary low-latency access for read-heavy workloads. Therefore, provisioned IOPS SSD is an excellent storage option for MongoDB.
B. General Purpose SSD: This storage option provides a balance between cost and performance for workloads that require low to moderate I/O operations. However, it is not recommended for high-performance applications or for applications that require consistent low latency, such as MongoDB. Hence, it may not be an ideal storage option for hosting a high-performance MongoDB database.
C. Throughput Optimized HDD (Hard Disk Drive): This storage option is designed for workloads that require high throughput for sequential read/write operations. However, it may not be suitable for high-performance applications with low-latency requirements, such as MongoDB. MongoDB requires low-latency access to storage, especially for write-intensive workloads, and HDDs are known to have higher latency than SSDs. Therefore, this storage option may not be the best fit for hosting MongoDB databases.
D. Cold HDD: This storage option is designed for infrequently accessed data or archival data. It has the lowest cost per GB but offers the lowest performance and lowest I/O operations per second (IOPS) compared to other storage options. It is not recommended for high-performance applications or workloads that require frequent access to data. Therefore, this storage option may not be suitable for hosting a high-performance MongoDB database.
In conclusion, the most suitable storage option for hosting a high-performance MongoDB database is Provisioned IOPS SSD.