Secure Solution for Communication Between Amazon S3 Buckets and DynamoDB
Question
A company has applications running in multiple VPCs.
These applications require interaction between Amazon S3 buckets and DynamoDB.
The company's security policy requires that communication should be secure and should not go over the public internet.
How does a solutions architect design this solution to meet these requirements?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: A.
Types of VPC endpoints for Amazon S3
You can use two types of VPC endpoints to access Amazon S3: gateway endpoints and interface endpoints.
A gateway endpoint is a gateway that you specify in your route table to access Amazon S3 from your VPC over the AWS network.
Interface endpoints extend the functionality of gateway endpoints by using private IP addresses to route requests to Amazon S3 from within your VPC, on-premises, or from a VPC in another AWS Region using VPC peering or AWS Transit Gateway.
There are two types of VPC endpoints:
Interface endpoint is an elastic network interface (ENI) with a private IP address from the IP address range of the user's subnet that serves as an entry point for traffic destined to a supported service.
It enables you to privately access services by using private IP addresses.
Gateway endpoint is a gateway that you specify as a target for a route in your route table for traffic destined to support AWS service.
Currently supports S3 and DynamoDB services.
Option A is CORRECT because the VPC gateway endpoint supports S3 and DynamoDB.
Using the VPC endpoint, communication will not go over the internet, and it will use AWS private network.
A VPC endpoint does not require an IGW, NAT device.
Instances in the VPC do not require public IP addresses to communicate with resources in the service.
Traffic between VPC and the other service stays in the Amazon network.
Option B is incorrect as NAT gateway and IGW use public internet and do not provide secure channels.
Option C is incorrect as DynamoDB can be accessed using Gateway endpoint and not interface endpoint.
VPC peering is between VPCs.
Option D is incorrect as S3 can be accessed using the Interface endpoint but the DynamoDB requires the gateway endpoint.
The option says to use the interface endpoint for both AWS S3 and the DynamoDB table.
References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/endpoint-service.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/privatelink-interface-endpoints.html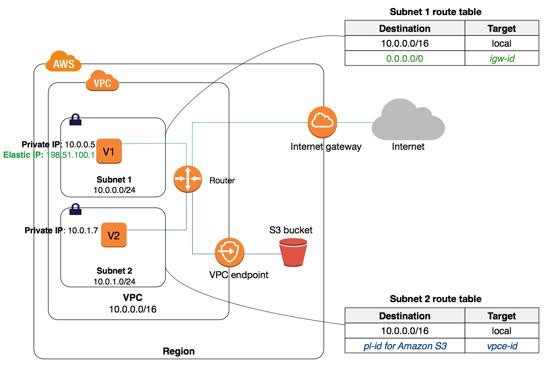
The requirement is to enable communication between Amazon S3 buckets and DynamoDB for applications running in multiple VPCs in a secure manner without going over the public internet. To achieve this, there are several options available, and the best solution depends on the specific needs and constraints of the company.
Option A: Create VPC Gateway Endpoints for S3 and DynamoDB and update route tables for all the availability zones.
A VPC Gateway Endpoint is a private endpoint for accessing AWS services over a direct and secure connection from within a VPC, without using an internet gateway, NAT device, or VPN connection. It allows traffic to flow between the VPC and the AWS service without traversing the internet.
To use this option, a VPC Gateway Endpoint must be created for both Amazon S3 and DynamoDB services. Once created, the route tables for all availability zones in the VPCs must be updated to ensure that traffic destined for these services is directed to the appropriate gateway endpoint.
This option is a good fit for scenarios where there are multiple VPCs that need to access S3 and DynamoDB services in a secure manner without going over the public internet.
Option B: Use the NAT Gateway and Internet Gateway for all the egress communication to these AWS services.
A NAT Gateway is a managed service that enables instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services, but prevents the internet from initiating a connection with those instances. An Internet Gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows communication between instances in the VPC and the internet.
To use this option, a NAT Gateway must be created in each VPC, and the instances in the VPC must be configured to use the NAT Gateway as the default route for all outbound traffic. An Internet Gateway must also be created to allow the NAT Gateway to access the AWS services over the internet.
This option is a good fit for scenarios where there are few VPCs and the traffic between the VPCs and the AWS services is relatively low.
Option C: Set up VPC peering and use VPC gateway endpoint for S3 and interface endpoint for DynamoDB to communicate over AWS network.
VPC peering is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables instances in one VPC to communicate with instances in the other VPC as if they were on the same network. To use this option, VPC peering must be established between the VPCs. Once the peering is established, VPC Gateway Endpoint for S3 and Interface Endpoint for DynamoDB can be created in the destination VPCs.
This option is a good fit for scenarios where there are two or more VPCs that need to communicate with each other and with AWS services in a secure manner.
Option D: Set up a VPC interface endpoint for both S3 and DynamoDB to communicate over the AWS network.
A VPC interface endpoint is an elastic network interface with a private IP address that serves as an entry point for traffic destined to an AWS service. When instances in a VPC access the AWS service, the traffic is directed to the VPC interface endpoint, which routes the traffic to the appropriate AWS service.
To use this option, a VPC interface endpoint must be created for both Amazon S3 and DynamoDB services. Once created, the instances in the VPC can communicate with the AWS services through the VPC interface endpoints.
This option is a good fit for scenarios where there are few VPCs and the traffic between the VPCs and the AWS services is relatively low.
In conclusion, the best option for the company depends on the specific needs and constraints. Option A is a good fit for scenarios where there are multiple VPCs that need to access S3 and DynamoDB services in a