One Availability Zone Not Receiving Traffic
Question
Your application has very high traffic.
So you have enabled autoscaling in multi-availability zone to suffice your application's needs.
But you observe that one of the availability zones is not receiving any traffic.
What can be wrong here?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - C.
In order to make sure that all the EC2 instances behind a cross-zone ELB receive the requests, make sure that all the applicable availability zones (AZs) are added to that ELB.Option A is incorrect because autoscaling can work with multiple AZs.
Option B is incorrect because autoscaling can be enabled for multi-AZ in any single region, not just N.
Virginia.
(see the image below)
Option C is CORRECT because most likely, the reason is that the AZ - whose EC2 instances are not receiving requests - is not added to the ELB.
Option D is incorrect because instances need not be added manually to AZ (they should already be there!).
More information on adding AZs to ELB.
When you add an Availability Zone to your load balancer, Elastic Load Balancing creates a load balancer node in the Availability Zone.
Load balancer nodes accept traffic from clients and forward requests to the healthy registered instances in one or more Availability Zones.
For more information on adding AZ's to ELB, please refer to the below URL-
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/classic/enable-disable-az.html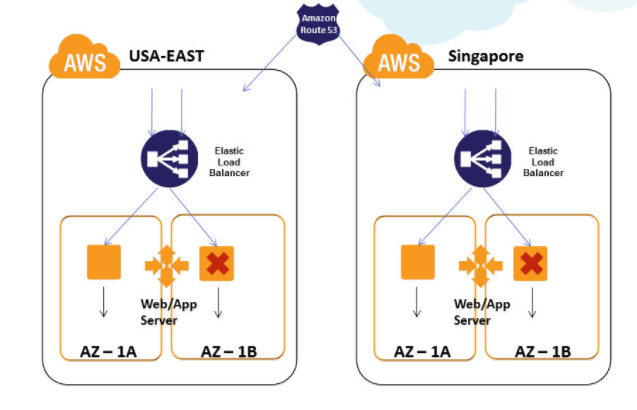
The correct answer to this question is C. Availability zone is not added to Elastic load balancer.
When autoscaling is enabled in multi-availability zone, it means that AWS will automatically launch and terminate instances across multiple availability zones based on the demand of the application. This ensures high availability and fault tolerance of the application.
In order for the traffic to be distributed across all the availability zones, the instances launched by the autoscaling group should be registered with an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB). The ELB is responsible for distributing the traffic across all the registered instances in all availability zones.
If one of the availability zones is not receiving any traffic, it may be because the instances in that zone are not registered with the ELB. This could be due to a misconfiguration of the ELB or the autoscaling group. To resolve this issue, you should check if the instances in the affected availability zone are registered with the ELB, and if not, add them to the ELB target group. You should also verify that the autoscaling group is configured to launch instances in all the required availability zones.
Option A, "Autoscaling only works for single availability zone", is incorrect because autoscaling can be enabled across multiple availability zones for high availability and fault tolerance.
Option B, "Autoscaling can be enabled for multi AZ only in north Virginia region", is incorrect because autoscaling can be enabled for multi AZ in any region that supports multiple availability zones.
Option D, "Instances need to manually added to availability zone", is incorrect because instances are automatically launched in the availability zones that are specified in the autoscaling group configuration.
