.NET Code Execution Against AWS on EC2 with IAM Role
Question
A company has an application that is hosted on an EC2 instance.
The code is written in .NET and connects to a MySQL RDS database.
If you're executing .NET code against AWS on an EC2 instance that is assigned an IAM role, which of the following is a true statement?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A.
The best practice for IAM is to create roles that have specific access to an AWS service and then give the user permission to the AWS service via the role.
For the best practices on IAM policies, please visit the links.
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/id_roles_use_switch-role-ec2.htmlNote:
As per AWS,
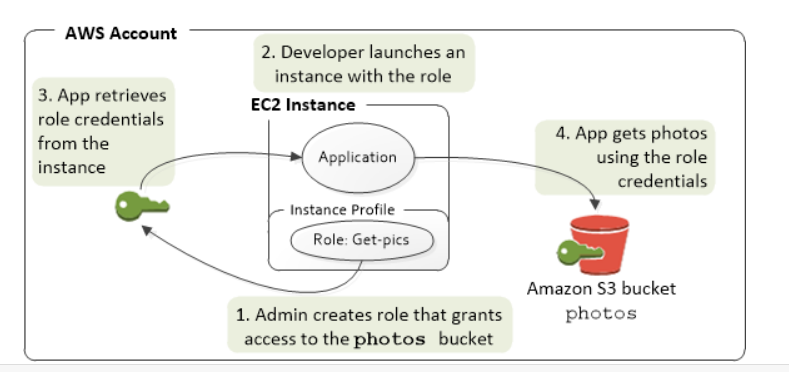
When you launch an EC2 instance, you specify an IAM role to associate with the instance.
Applications that run on the instance can then use the role-supplied temporary credentials to sign API requests.
Using roles to grant permissions to applications that run on EC2 instances requires a bit of extra configuration.
An application running on an EC2 instance is abstracted from AWS by the virtualized operating system.
Because of this extra separation, an additional step is needed to assign an AWS role and its associated permissions to an EC2 instance and make them available to its applications.
This extra step is the creation of an instance profile that is attached to the instance.
The instance profile contains the role and can provide the role's temporary credentials to an application that runs on the instance.
Those temporary credentials can then be used in the application's API calls to access resources and limit access to only those resources that the role specifies.
Note that, only one role can be assigned to an EC2 instance at a time, and all applications on the instance share the same role and permissions.
The example given here shows how the application retrieves role permissions from the instance for accessing the bucket.
The correct answer is A. Retrieve the temporary security credentials from Amazon EC2 instance metadata. These are then passed on to the code that assumes the role and is valid for a limited time.
When an EC2 instance is assigned an IAM role, it can use the AWS SDK or CLI to retrieve temporary security credentials from the instance metadata service. These credentials include an access key, a secret access key, and a session token, and are valid for a limited time, usually one hour.
In this scenario, the .NET code running on the EC2 instance can use the AWS SDK for .NET to retrieve the temporary security credentials and assume the IAM role. Once the code assumes the role, it can access AWS resources as defined by the permissions of the IAM role.
Option B is incorrect because the code does not need to have AWS access keys to execute if it is running on an EC2 instance with an assigned IAM role. The IAM role provides temporary security credentials that can be used to access AWS resources.
Option C is incorrect because IAM roles can be assumed by any AWS SDK, not just .NET code. For example, Python, Java, and Ruby SDKs can also assume IAM roles.
Option D is incorrect because the correct answer is A, as explained above.