Secure Two-Tier Web Application with MySQL
Question
Your supervisor tells you of a client who needs a two-tier web application that is publicly accessible and configured on AWS.
The most important requirement is that MySQL must be used as the database, and it must be configured at the client's location in the most secure fashion.
Which of the following solutions would be the best to ensure that the client's requirements are met?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A.
In this scenario, the main architectural consideration is that the database should remain on the client's data center.
Since the database should not be hosted on the cloud, you cannot put the database in the public subnet in AWS.
Option A is correct because it puts the application servers in the public subnet ( because it should be publicly accessible ) and keeps the database server at the client's data center.
This is also a valid two-tiered architecture.
Option B is INCORRECT because VPC peering cannot establish the connection between on-premises and AWS VPC.Option C is INCORRECT because the database cannot be on the public subnet.
It is rather located at the client's data center as per the question.
Option D is INCORRECT because the database cannot be on the public subnet due to the posed security risk (against the question's requirements).
The best option is to create a VPN connection for securing traffic, as shown below.
For more information on VPN connections, please visit the below URL-
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonVPC/latest/UserGuide/VPC_VPN.html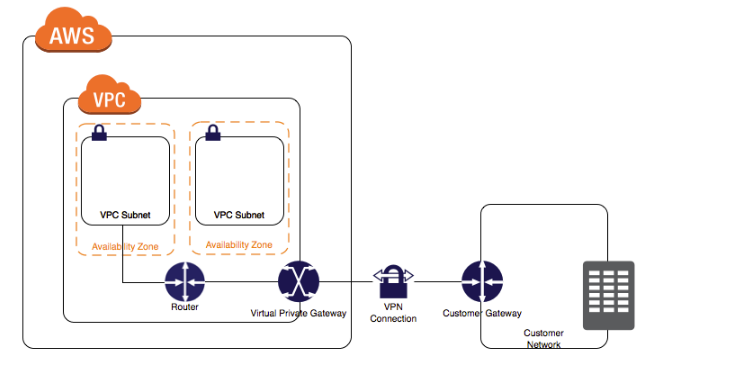
The best solution to meet the client's requirements for a two-tier web application using MySQL as the database on AWS would be option A. Building the application server on a public subnet and the database at the client's data center, and connecting them using a VPN connection that uses IPsec.
Option A provides a secure solution for the client's requirement for a two-tier web application. By building the application server on a public subnet, it can be accessed from the internet. At the same time, the database is located in the client's data center, which ensures that the client has complete control over the database and its security.
Connecting the application server and the database with a VPN connection that uses IPsec ensures that the connection between the two is encrypted, providing a secure connection between the two systems. Additionally, by building the application server on a public subnet, the client can configure the necessary security groups to allow traffic only from authorized sources.
Option B, building the application server on a private subnet and the database at the client's data center, and connecting them with a VPC peering connection, does not meet the requirement of the database being publicly accessible. This option does not provide a public IP address to the database, and hence the database cannot be accessed from the internet.
Option C, building the application server on a private subnet and the database on the public subnet with a NAT instance between them, is not the best solution for the client's requirement. This option involves using a NAT instance to enable the application server to access the internet, and hence the database. However, this introduces additional latency, and the NAT instance can become a single point of failure.
Option D, building the application server on the private subnet and the database on the public subnet with a secure SSH connection to the public subnet from the client's data center, is not the best solution. This option involves using a secure SSH connection to access the public subnet, which introduces additional security risks. Additionally, the database is publicly accessible, which may not meet the client's security requirements.
In summary, option A, building the application server on a public subnet and the database at the client's data center, and connecting them with a VPN connection that uses IPsec, is the best solution to meet the client's requirement for a two-tier web application using MySQL as the database on AWS.