Private Subnet Database Security Group Configuration (DBSecGrp)
Question
A user has created a VPC with the public and private subnets using the VPC wizard.
The VPC has CIDR 10.0.0.0/16
The public subnet uses CIDR 10.0.1.0/24
The user plans to host a web server in the public subnet with port 80 and a Database server in the private subnet with port 3306
The user is configuring a security group for the public subnet (WebSecGrp) and the private subnet (DBSecGrp)
Which of the below mentioned entries is required in the private subnet database security group DBSecGrp?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A.
The important point in this question is to allow the incoming traffic to the private subnet on port 3306 only for the instances in the private subnet.
Option A is CORRECT because (a) it allows the inbound traffic only for the required port 3306, and (b) it allows only the traffic from the instances in the public subnet (WebSecGrp).
Option B is incorrect because it allows the inbound traffic to all the instances in the VPC which is not the requirement.
Option C is incorrect because defining outbound traffic will not ensure the incoming traffic from the public subnet.
Also, since the security groups are stateful, you need to define the inbound traffic for the public subnet only (WebSecGrp)
The outbound traffic would be automatically allowed.
Option D is incorrect because you do not need to open the port 80 in this case.
More information on Web Server and DB Server Security Group settings:
Since the Web server needs to talk to the database server on port 3306, the database server should allow incoming traffic on port 3306
The below table from the AWS documentation shows how the security groups should be set up.
For more information on security groups, please visit the below link.
http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonVPC/latest/UserGuide/VPC_Scenario2.html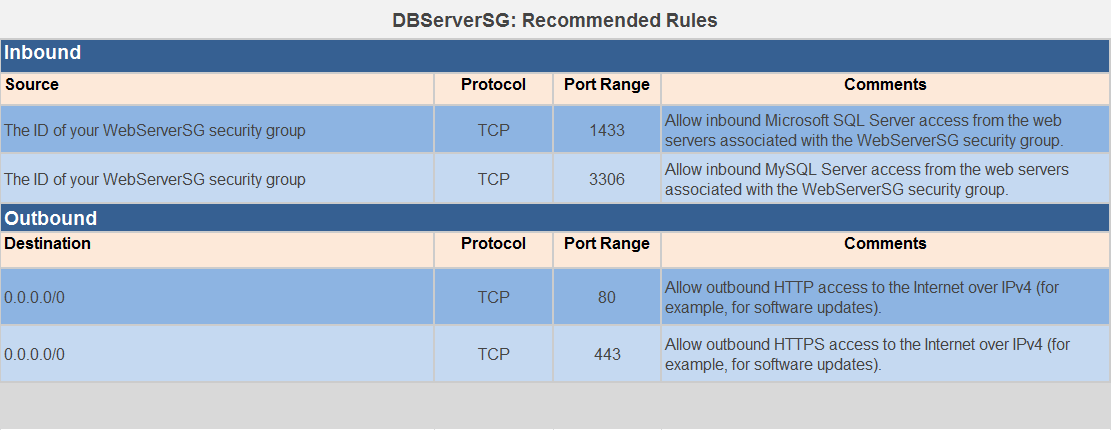
To allow communication between the web server in the public subnet and the database server in the private subnet, the user needs to create two security groups: one for the web server (WebSecGrp) and another for the database server (DBSecGrp). The security group rules should be configured to allow the necessary traffic to flow between the two servers.
Option A: Allow Inbound on port 3306 in the DBSecGrp with source as WebSecGrp.
This option is correct. The user needs to allow inbound traffic on port 3306 (MySQL) in the DBSecGrp security group from the WebSecGrp security group. This will allow the web server to communicate with the database server. By specifying the source as WebSecGrp, the user ensures that only traffic from the web server is allowed, and traffic from other sources is blocked.
Option B: Allow Inbound on port 3306 from source 10.0.0.0/16.
This option is not recommended because it allows traffic from any source within the VPC. While this may work, it is not a good security practice because it allows any instance within the VPC to connect to the database server.
Option C: Allow Outbound on port 3306 in the DBSecGrp with destination as WebSecGrp.
This option is not required. Outbound traffic is allowed by default in a security group, so the user does not need to create a rule to allow outbound traffic from the database server to the web server.
Option D: Allow Outbound on port 80 for destination NAT instance IP.
This option is not related to the communication between the web server and the database server. It is a rule that would be used to allow outbound traffic from the web server to a NAT instance, which is used for instances in a private subnet to communicate with the internet.
In summary, the correct answer is A. Allow Inbound on port 3306 in the DBSecGrp with source as WebSecGrp.