Key Statistics of Video Game Web Page Analytics
Question
You work in a video game company, and your team is working on a feature that tells how many times certain web pages have been viewed or clicked.
You also created an AWS Lambda function to show some key statistics of the data.
You tested the Lambda function, and it worked perfectly.
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Correct Answer- A.
Potentially, more than one option may work.
However, this question asks the most cost-efficient and straightforward method that needs to be considered.
Option A is CORRECT because the AWS CloudWatch Events rule is free and quite easy to begin with.
To schedule a daily event at 8:00 AM GMT, you just need to set up a cron rule, as given in the below screenshot.
Option B is incorrect: Because launching a new EC2 instance for this task is not cost-efficient.
Option C is incorrect: Because this is not something AWS Batch works.
For AWS Batch, it runs as a containerized application on an Amazon EC2 instance in your computing environment.
Option D is incorrect: Because firstly, it should be “Create rule” rather than “Create Event”
Secondly, the Cron expression of “ * ? * * 08 00” is incorrect.
For More information, Please check below AWS Docs:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudWatch/latest/events/ScheduledEvents.html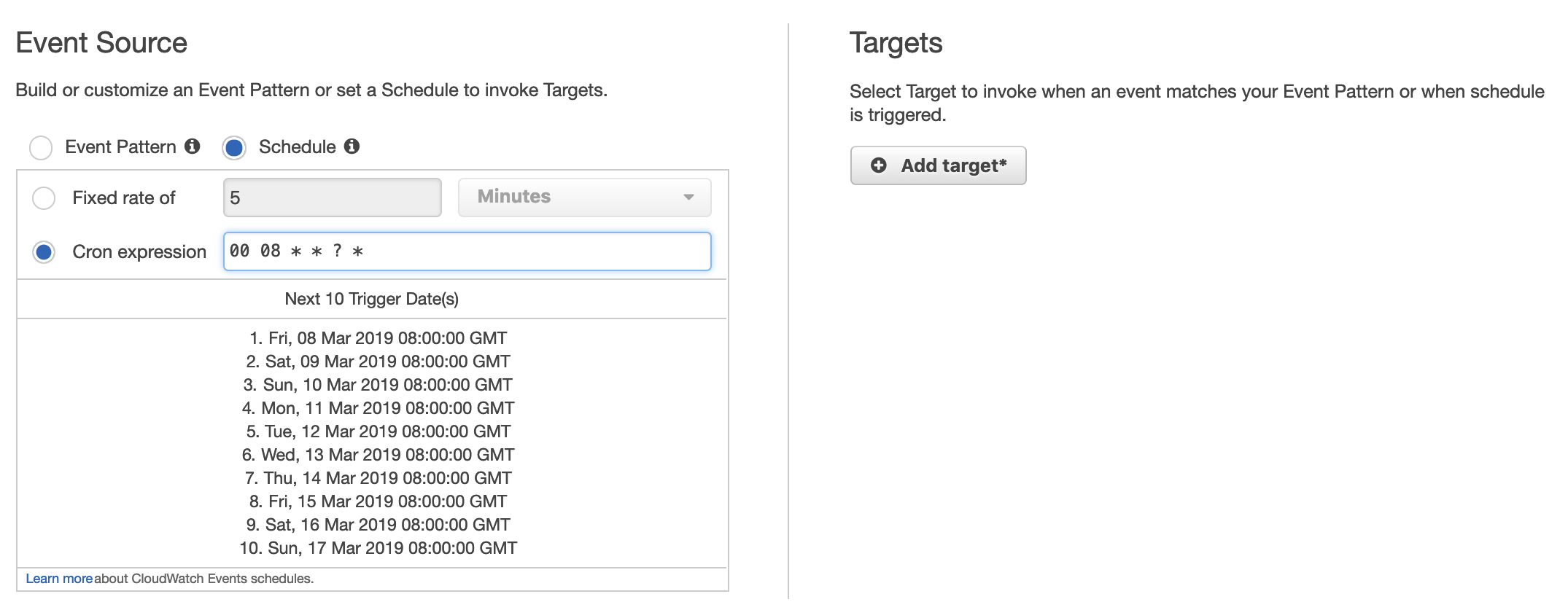
The best option for this scenario would be option D: In AWS CloudWatch Events console, click “Create Event” using the cron expression “ * ? * * 08 00”. Configure the target as the Lambda function.
Explanation: AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that allows developers to run code without the need to provision or manage servers. AWS Lambda integrates with other AWS services, such as Amazon S3, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Kinesis, to trigger code execution based on events from these services. AWS CloudWatch Events is a service that can be used to schedule and trigger events based on time, resource state changes, or custom events.
Option A: Create an AWS CloudWatch Events rule that is scheduled using a cron expression. Configure the target as the Lambda function. This option is almost correct, as it uses AWS CloudWatch Events to trigger the Lambda function based on a scheduled cron expression. However, it doesn't provide a specific cron expression to run the Lambda function at 8:00 AM, which is required in the scenario. It is possible to create a cron expression for 8:00 AM using this option, but it requires more effort.
Option B: Create an Amazon Linux EC2 T2 instance and set up a Cron job using Crontab. Use AWS CLI to call your AWS Lambda every 8:00 AM. This option is not ideal for this scenario because it requires setting up and managing an EC2 instance, which increases the operational cost and complexity. Additionally, it doesn't use AWS CloudWatch Events, which is the recommended way to schedule Lambda functions.
Option C: Use Amazon Batch to set up a job with a job definition that runs every 8:00 AM for the Lambda function. This option is also not ideal for this scenario because Amazon Batch is mainly used for running batch computing workloads at scale, and it requires more setup and management compared to AWS CloudWatch Events. It is also not the recommended way to schedule Lambda functions.
Option D: In AWS CloudWatch Events console, click “Create Event” using the cron expression “ * ? * * 08 00”. Configure the target as the Lambda function. This option is the best one for this scenario because it uses AWS CloudWatch Events to schedule the Lambda function execution based on a cron expression that runs at 8:00 AM. It also requires minimal setup and management, making it a cost-effective and efficient solution. The AWS CloudWatch Events console makes it easy to create and manage rules, and it integrates seamlessly with Lambda functions, making it the recommended solution for scheduling Lambda functions.