AWS CloudWatch Scheduled Event and Lambda Function
Question
You are planning to schedule a daily job with AWS CloudWatch scheduled event and AWS Lambda function triggered by the event that will perform a daily health check on your applications running on a fleet of EC2 instances.
To achieve this, you need to provide the EC2 instances' name tags to identify the right resources.
What is the correct way of passing the inputs in this case?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: C.
When using an AWS Cloudwatch rule to trigger a Lambda event, one of the multiple options you have to pass data onto your Lamba function is “Constant (JSON Text)”
This handy feature allows you to send static content to your function instead of the matched event.
You can also create the input targets via the CLI:
aws events put-targets --rule testjson --targets file://targetfile.
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/compute/simply-serverless-use-constant-values-in-cloudwatch-event-triggered-lambda-functions/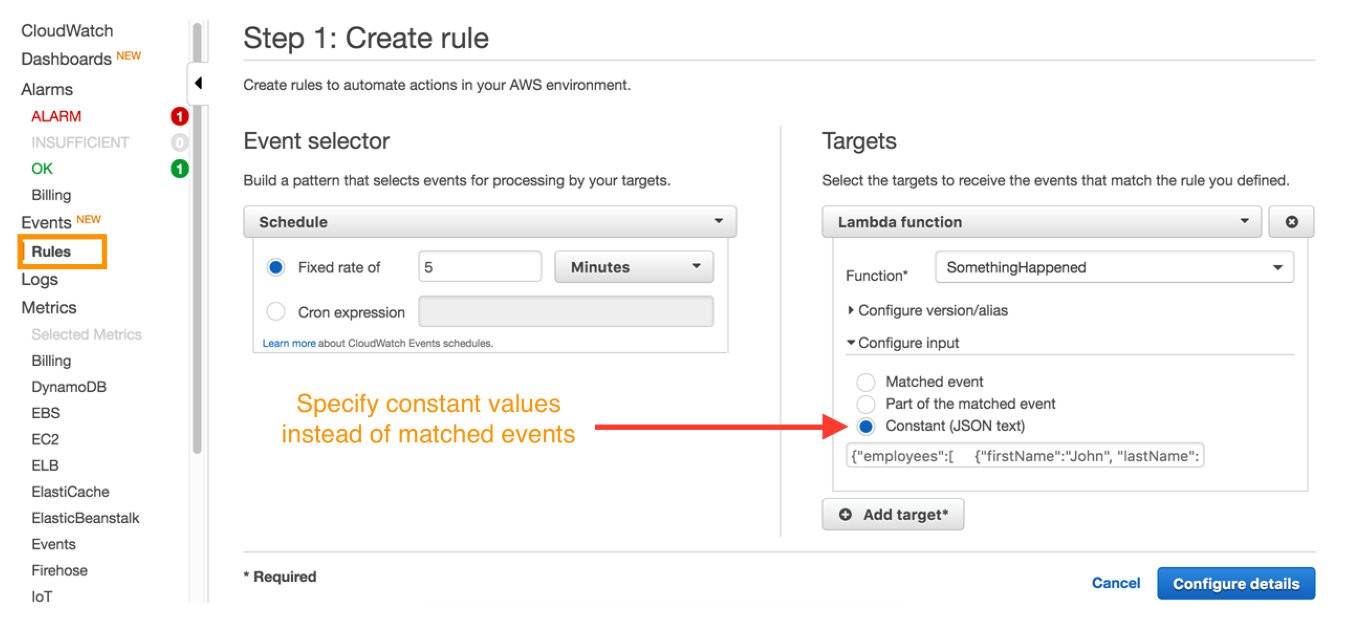
In order to schedule a daily job with AWS CloudWatch scheduled event and AWS Lambda function triggered by the event that will perform a daily health check on your applications running on a fleet of EC2 instances, you need to provide the EC2 instances' name tags to identify the right resources.
The correct way of passing the inputs in this case is option C: You can set the "Constant (JSON text)" option while configuring the AWS Cloudwatch rule to trigger a Lambda function from AWS CloudWatch scheduled event.
Here's how to configure this option:
- Navigate to the AWS CloudWatch console.
- Click on "Rules" in the left-hand menu.
- Click "Create rule" to create a new rule.
- In the "Event Source" section, select "Schedule" as the Event Source Type.
- Configure the "Fixed rate of" field to define how often the rule will be triggered.
- In the "Targets" section, click "Add target".
- Select "Lambda function" as the target type.
- Select your Lambda function from the dropdown list.
- In the "Configure input" section, select "Constant (JSON text)".
- Enter the name tag of your EC2 instances in JSON format, for example:
{ "tagKey": "Name", "tagValue": "myEC2Instance" }
This will pass the name tag "myEC2Instance" to your Lambda function, which can then use it to identify the correct EC2 instance for performing the health check.
Option A, configuring the "Variables" option on the AWS CloudWatch scheduled event, is not correct because this option is not available for a scheduled event. Option B, modifying the "Matched Event" option while selecting AWS Lambda as the trigger for CloudWatch scheduled event, is not correct because the "Matched Event" option is used for event pattern matching, not for passing inputs to Lambda functions. Option D, configuring the "Details" object of "Matched Event" while creating an AWS CloudWatch scheduled event, is not correct because the "Details" object is used for passing event data to the Lambda function, not for passing inputs.
