Customers' Responsibilities in AWS
Question
In AWS, which security aspects are the customers' responsibility? Choose 4 answers from the options given below.
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D. E. F.Answer - A, C, D and.
F.Below is the snapshot of the AWS Shared Responsibility Model:
For more information on the Shared Responsibility Model, please refer to the below URL:
https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/shared-responsibility-model/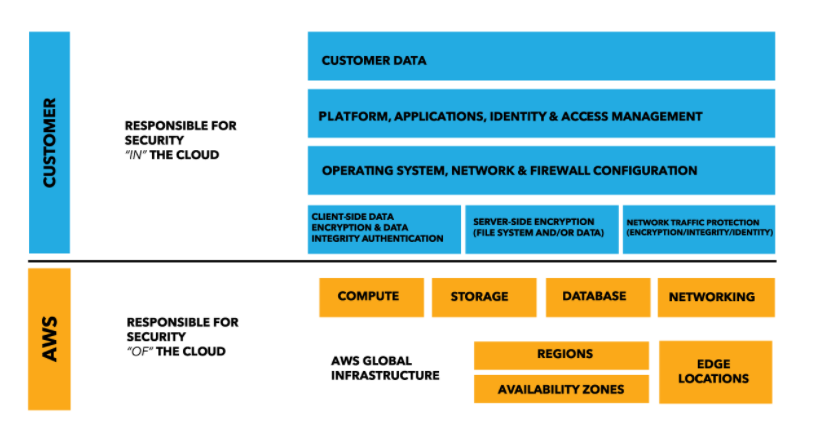
In AWS, the shared responsibility model defines the security responsibilities between AWS and its customers. AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure that includes hardware, software, and networking. While customers are responsible for securing their own data and applications that they deploy on AWS.
The following are the four security aspects that are the customer's responsibility in AWS:
A. Security Group and ACL (Access Control List) settings: Customers are responsible for managing their security groups and access control lists (ACLs) to ensure that only authorized traffic is allowed to access their instances. AWS provides a network-based firewall that controls traffic to instances, but customers are responsible for configuring security groups and ACLs to enforce additional security policies as required.
B. Decommissioning storage devices: Customers are responsible for decommissioning storage devices when they are no longer needed. AWS provides secure deletion mechanisms that ensure that data is unrecoverable when a storage device is decommissioned, but customers must ensure that they follow best practices to remove any sensitive data from the storage devices before they are decommissioned.
C. Patch management on the EC2 instance's operating system: Customers are responsible for ensuring that the operating system of their EC2 instances is patched and up-to-date with the latest security updates. AWS provides managed services such as Amazon EC2 Systems Manager that enable customers to automate patch management, but customers are responsible for configuring and managing these services.
D. Life-cycle management of IAM credentials: Customers are responsible for managing the life-cycle of their IAM (Identity and Access Management) credentials, including creating and deleting IAM users, and rotating access keys regularly to ensure that only authorized users have access to AWS resources. AWS provides tools such as AWS IAM that enable customers to manage IAM credentials, but customers are responsible for configuring and managing these tools.
The following are the security aspects that are AWS's responsibility:
E. Controlling physical access to compute resources: AWS is responsible for controlling physical access to compute resources such as data centers and servers. AWS employs various physical security measures such as security cameras, biometric authentication, and security guards to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to AWS resources.
F. Encryption of EBS (Elastic Block Storage) volumes: AWS is responsible for encrypting EBS volumes at rest using industry-standard encryption algorithms. AWS provides various encryption mechanisms such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS) that enable customers to encrypt their data at rest and in transit, but customers are responsible for configuring and managing these mechanisms.