Setting Permissions for Lambda Trigger across AWS Accounts
Question
Your organization has two accounts, for DEV and TEST.
You have certain user applications running on the TEST account would like to trigger AWS Lambda on the DEV account.
What is the permission model which needs to be set to get this configuration working?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: A.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/access-control-resource-based.html?shortFooter=true#access-control-resource-based-example-cross-account-scenarioOptions B, C are not correct.
Permission needs to be added to the Lambda function policy to invoke the function, not on the execution role policy.
Option D is not correct.
Lambda function policy cannot be edited from the AWS console.
For more information, please fere to the below mentioned AWS docs:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/access-control-resource-based.html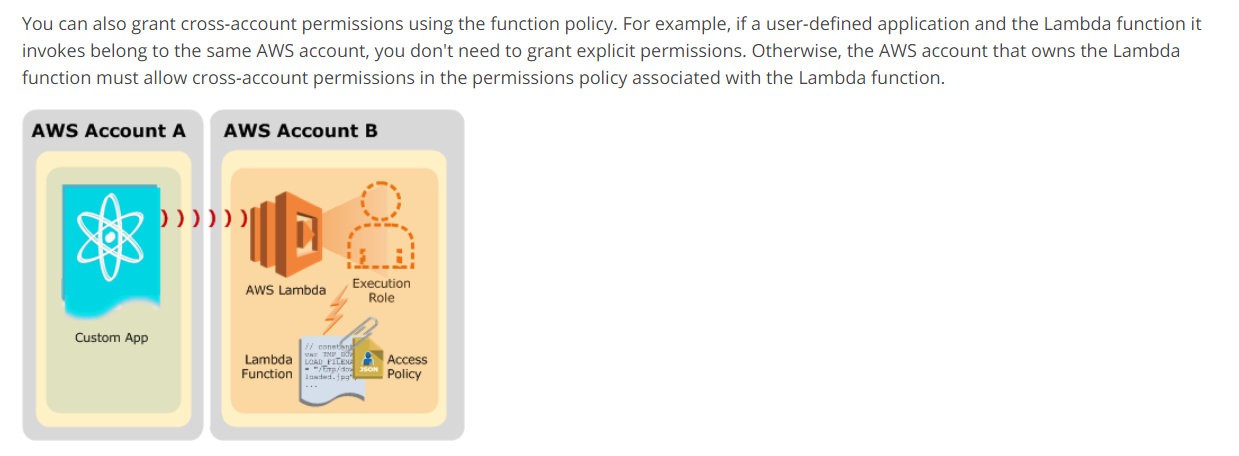
In order for an application running on the TEST account to trigger an AWS Lambda function on the DEV account, you need to grant permission to the TEST account to invoke the Lambda function on the DEV account.
The AWS Lambda function policy controls who can invoke the Lambda function. The policy must include an IAM role or user that has permission to invoke the Lambda function. You can add permissions to the Lambda function policy using either the AWS CLI or the AWS Management Console.
Option A suggests adding permissions for the TEST account to the DEV account's Lambda function policy using the AWS CLI. This is incorrect because the Lambda function policy is only used to control access to the function itself, and not to control access to invoke the function.
Option B suggests adding permissions for the TEST account to the DEV account's Lambda execution role policy through the AWS Management Console. This is partially correct. The Lambda execution role policy controls who or what can execute the Lambda function. By adding the TEST account to the execution role policy, you are granting permission for the TEST account to invoke the Lambda function on the DEV account. However, the question specifically asks for the permission model that needs to be set, and this answer only addresses part of the required permission model.
Option C suggests adding permissions for the TEST account to the DEV account's Lambda execution role policy using the AWS CLI. This is the correct answer. The Lambda execution role policy controls who or what can execute the Lambda function, and adding the TEST account to the execution role policy using the AWS CLI will grant permission for the TEST account to invoke the Lambda function on the DEV account.
Option D suggests adding permissions for the TEST account to the DEV account's Lambda function policy using the AWS Management Console. This is incorrect for the same reasons as Option A.
In summary, the correct answer is option C. You need to add permission for the TEST account on the DEV account's Lambda execution role policy through the AWS CLI to allow an application running on the TEST account to trigger an AWS Lambda function on the DEV account.