Choose the Right EBS Storage Type for Your Big Data Project
Question
Your organization is planning to build a BigData project on AWS.
They need high data transfer rates for huge workloads to stream through with better performance.They are also looking for a cost-effective solution.
Which EBS storage type would you choose in this scenario?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: C.
Amazon EBS provides the following volume types, which differ in performance characteristics and price, so that you can tailor your storage performance and cost to the needs of your applications.
The volumes types fall into two categories:
SSD-backed volumes optimized for transactional workloads involving frequent read/write operations with small I/O size, where the dominant performance attribute is IOPS.
HDD-backed volumes optimized for large streaming workloads where throughput (measured in MiB/s) is a better performance measure than IOPS.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/WindowsGuide/EBSVolumeTypes.html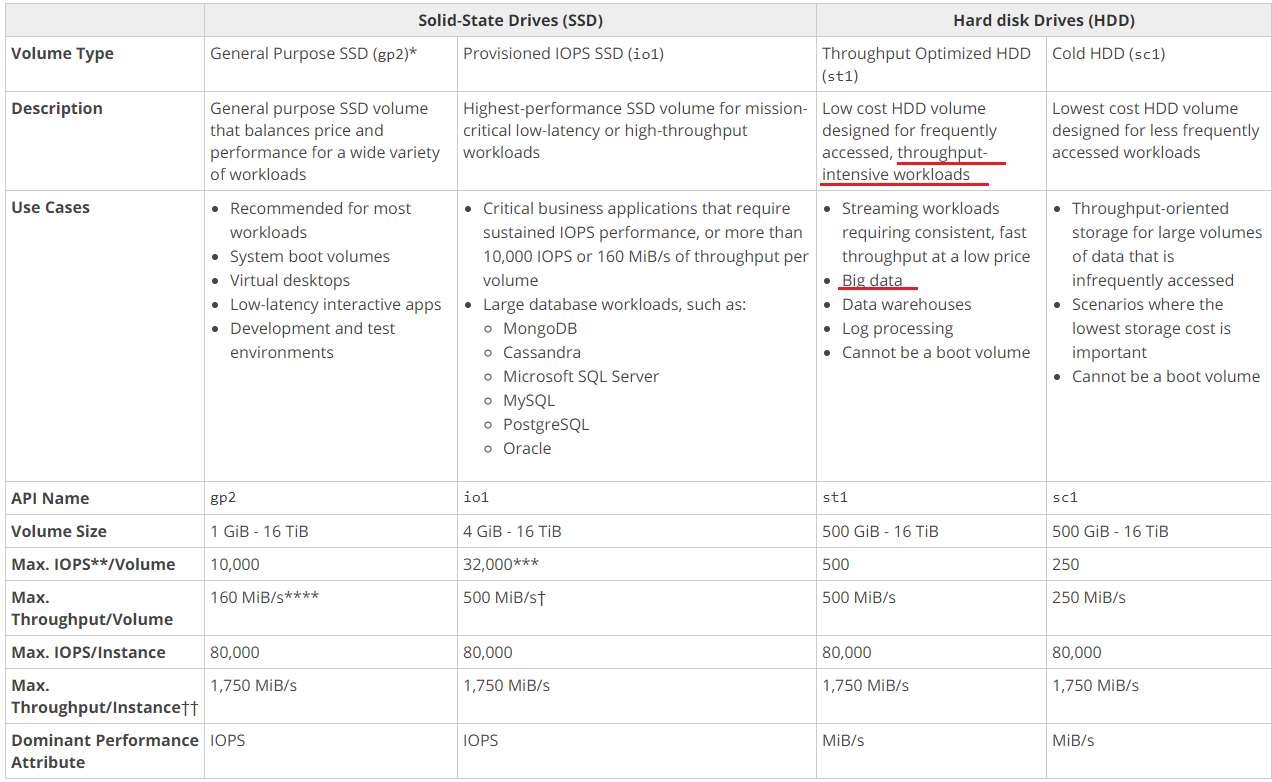
For a BigData project on AWS that requires high data transfer rates for huge workloads with better performance, and cost-effectiveness, the recommended EBS storage type would be the "Throughput Optimized HDD" (C).
Throughput Optimized HDDs are designed to provide low-cost storage with high throughput and are optimized for frequently accessed, large streaming workloads. This storage type is ideal for BigData workloads such as log processing, data warehousing, and big data analytics that require high-performance and low-cost storage.
The "General Purpose SSD" (A) is best suited for small to medium-sized workloads with moderate I/O requirements. Provisioned IOPS SSD (B) is designed for workloads that require consistent and high IOPS performance, such as large databases, NoSQL databases, and transactional workloads. These two options may not be cost-effective for the BigData project since they are more expensive than the Throughput Optimized HDD.
"Cold HDD" (D) is designed for infrequent access and long-term storage, making it a poor choice for BigData workloads that require frequent access and high-performance storage.
Therefore, the Throughput Optimized HDD is the most suitable and cost-effective option for a BigData project with high data transfer rates, huge workloads, and better performance.