Architecting a Web Server and RDS Instance on AWS | SAA-C03 Exam Answer
Question
Your organization is planning to develop a web application containing a Web Server and an RDS Instance.
This application will be accessed from the internet.
Your organization asked you to architect the solution on AWS.
Your existing AWS environment already has a VPC with a private subnet and public subnet which has a route to the internet through Internet Gateway.
What would be the best and cost-effective solution you can provide?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: D.
An Elastic IP address is a static, public IPv4 address designed for dynamic cloud computing.
With an Elastic IP address, you can mask the failure of an instance by rapidly remapping the address to another instance in your VPC.Option A, EC2 instances in the private subnet cannot be reached from the internet.
A bastion host is a server whose purpose is to provide access to a private network from an external network, such as the Internet.
It does not act as a proxy to route traffic from the internet to private EC2 instances.
AWS Document says:
Amazon VPC enables you to launch AWS resources on a virtual private network that you have defined.
The bastion host runs on an Amazon EC2 instance, typically in a public subnet of your Amazon VPC.
Linux instances are in a subnet that is not publicly accessible.
They are set up with a security group that allows SSH access from the security group attached to the underlying EC2 instance running the bastion host.
Bastion host users connect to the bastion host to connect to the Linux instances, as illustrated in the following diagram.
Option B, with EC2 instance in the public subnet and Elastic IP attached, traffic from the internet can reach Web Server, and application works well.
Although this option looks correct, this is not cost-effective since there is no use of Bastion host anywhere since the EC2 instance is already in the public subnet.
Option C, Same as option A.
Although we have NAT Gateway attached to the subnet where Web Server EC2 resides, the traffic from the internet cannot reach the EC2, and NAT Gateway only routes traffic from AWS resources within a VPC to the internet.
Any traffic from the internet into VPC resources is not allowed by NAT Gateway.
Option D, the Web Server EC2 instance is in public subnet with elastic IP address attached to it and RDS in private subnet which cannot be reached from the internet but only can allow traffic from EC2 in public subnet via security groups.
For more information on the Elastic IP address, please refer to the documentation.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/elastic-ip-addresses-eip.html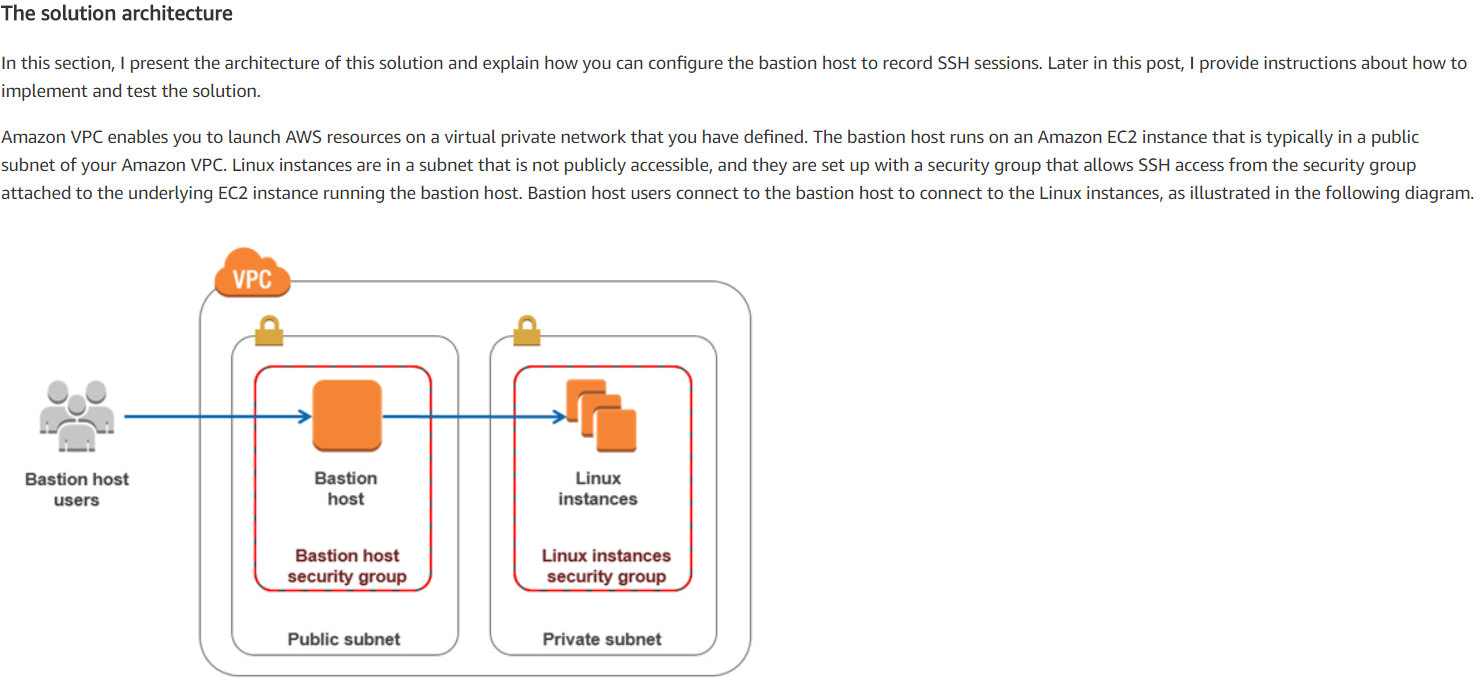
The best and cost-effective solution would be option C.
Explanation:
Option A: This option proposes to place the Web Server EC2 instance in the private subnet, which provides better security, but the problem is that there is no way to access it from the internet. So, to manage the server, a Bastion host is proposed to be placed in the public subnet. However, this solution adds additional costs as a separate EC2 instance needs to be launched, and also it may have security concerns.
Option B: This option places the Web Server EC2 instance in the public subnet, which means it can be directly accessed from the internet. However, this is not a secure way of implementing it. So, to access it securely, a Bastion host is proposed to be placed in the public subnet, which again adds additional costs as a separate EC2 instance needs to be launched.
Option C: This option places the Web Server EC2 instance in the private subnet with a NAT Gateway, which allows outbound internet traffic from the private subnet. This option is secure because the Web Server is not directly exposed to the internet. To manage the server, a Bastion host is proposed to be placed in the public subnet, which can be accessed from the internet.
Option D: This option places the Web Server EC2 instance in the public subnet, which means it can be directly accessed from the internet. However, this is not a secure way of implementing it. So, it is not a recommended solution.
In summary, option C is the best and cost-effective solution. The Web Server EC2 instance can be placed in the private subnet with a NAT Gateway, and a Bastion host can be placed in the public subnet to manage it securely. The RDS instance can also be placed in the private subnet, which provides better security.