Addressing Potential Security Threat of Non-Encrypted EFS Volume
Question
An IT company has a big data analytics application that is deployed in EC2 in multiple availability zones.
These EC2 instances simultaneously access a shared Amazon EFS file system using a traditional file permissions model.
A recent internal security audit has found a potential security risk, as the EFS file system is not encrypted for either at rest or in transit.
What actions could be taken to address the potential security threat posed by the non-encryption of the EFS volume?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Correct Answer - A.
Both encryption of data in transit and at rest are supported for EFS.
Due to this, Amazon EFS now offers a comprehensive encryption solution.
Blog https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-encryption-of-data-in-transit-for-amazon-efs/ has an introduction to this.
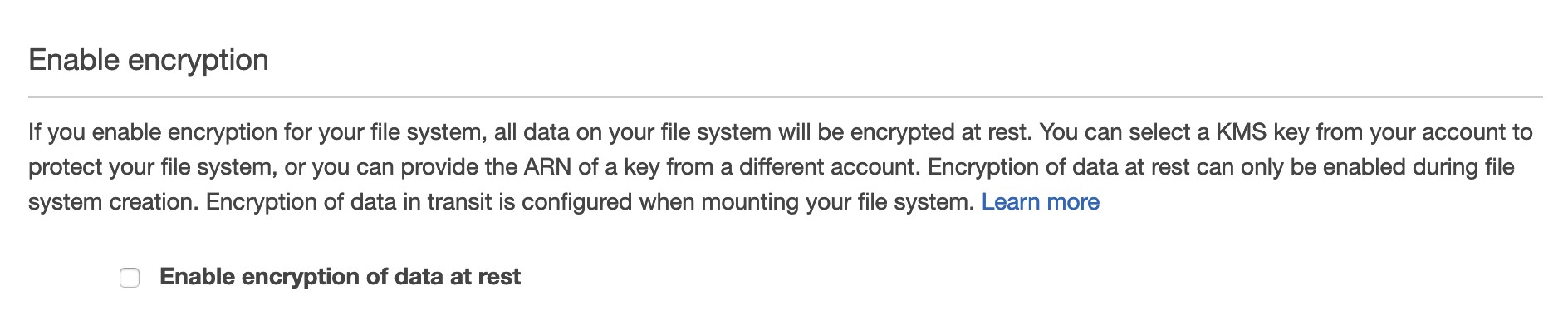
Option A is CORRECT: For the encryption at rest, it can be enabled as an option when the EFS file system is created.
For the encryption in transit, it can be enabled when the EFS file system is mounted:
sudo mount -t efs-o tls fs-12345678:/ /mnt/efs.
Reference is in https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/encryption.html.
Option B is incorrect: Because the encryption of data in transit is enabled when the EFS file system is mounted.
Option C is incorrect: Because the encryption of data at rest is enabled when the EFS file system is created.
Option D is incorrect: Same reason as Option B &
C.
Sure, I'd be happy to explain this question in detail!
First, let's briefly discuss what Amazon EFS is and how it works. Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is a scalable, fully managed, cloud-based NFS file system that provides shared access to files across multiple EC2 instances. EFS allows for easy access to shared file storage from multiple EC2 instances, which is especially useful for big data analytics applications that require a shared storage system.
Now, let's look at the question. The IT company in question has deployed a big data analytics application in EC2 across multiple availability zones, with all instances accessing a shared Amazon EFS file system using traditional file permissions. The internal security audit has found a potential security risk because the EFS file system is not encrypted for either at rest or in transit.
To address this potential security risk, the question asks what actions could be taken. Let's look at each answer option in turn:
A. The encryption of data at rest has to be enabled when the Amazon EFS file system is created. The encryption of data in transit can be enabled when the file system is mounted in the EC2 instance.
This answer option is incorrect. While it is true that data at rest can be encrypted when an EFS file system is created, data in transit cannot be enabled when the file system is mounted. Encryption of data in transit requires the use of a secure network protocol, such as SSL/TLS or IPsec, which must be configured separately from the file system.
B. The encryption of data at rest and in transit can be enabled when the Amazon EFS file system is created.
This answer option is correct. When creating an EFS file system, you can enable encryption of data at rest and in transit. Encryption of data at rest is done using AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and encryption of data in transit is done using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS).
C. The encryption of data at rest and in transit can only be enabled when the Amazon EFS file system is mounted in the EC2 instance.
This answer option is incorrect. Encryption of data at rest and in transit can be enabled when the EFS file system is created, not just when it is mounted in the EC2 instance.
D. The encryption of data at rest can be enabled when the Amazon EFS file system is mounted in the EC2 instance. The encryption of data in transit is enabled when the EFS file system is created using the AWS console or CLI.
This answer option is incorrect. Encryption of data at rest and in transit can both be enabled when the EFS file system is created, not just when it is mounted in the EC2 instance.
So, the correct answer is B. The encryption of data at rest and in transit can be enabled when the Amazon EFS file system is created. By enabling encryption of data at rest and in transit, the IT company can address the potential security risk posed by the non-encryption of the EFS volume, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of the data stored in the file system.
