Corrective Actions on Significant Differences in PDCA Cycle
Question
Which of the following step of PDCA request a corrective actions on significant differences between the actual versus the planned result?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.D.
Act - Request corrective actions on significant differences between actual and planned results.
Analyze the differences to determine their root causes.
Determine where to apply changes that will include improvement of the process or product.
When a pass through these four steps does not result in the need to improve, the scope to which PDCA is applied may be refined to plan and improve with more detail in the next iteration of the cycle, or attention needs to be placed in a different stage of the process.
For your exam you should know the information below: PDCA (plan"do"check"act or plan"do"check"adjust) is an iterative four-step management method used in business for the control and continuous improvement of processes and products.
It is also known as the Deming circle/cycle/wheel, Stewart cycle, control circle/cycle, or plan"do"study"act (PDSA)
Another version of this PDCA cycle is OPDCA.
The added "O" stands for observation or as some versions say "Grasp the current condition." The steps in each successive PDCA cycle are:
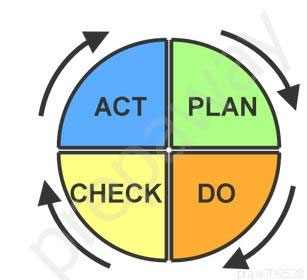
PLAN - Establish the objectives and processes necessary to deliver results in accordance with the expected output (the target or goals)
By establishing output expectations, the completeness and accuracy of the spec is also a part of the targeted improvement.
When possible start on a small scale to test possible effects.
DO - Implement the plan, execute the process, make the product.
Collect data for charting and analysis in the following "CHECK" and "ACT" steps.
CHECK - Study the actual results (measured and collected in "DO" above) and compare against the expected results (targets or goals from the "PLAN") to ascertain any differences.
Look for deviation in implementation from the plan and also look for the appropriateness and completeness of the plan to enable the execution, i.e., "Do"
Charting data can make this much easier to see trends over several PDCA cycles and in order to convert the collected data into information.
Information is what you need for the next step "ACT"
ACT - Request corrective actions on significant differences between actual and planned results.
Analyze the differences to determine their root causes.
Determine where to apply changes that will include improvement of the process or product.
When a pass through these four steps does not result in the need to improve, the scope to which PDCA is applied may be refined to plan and improve with more detail in the next iteration of the cycle, or attention needs to be placed in a different stage of the process.
The following answers are incorrect: PLAN - Establish the objectives and processes necessary to deliver results in accordance with the expected output (the target or goals)
DO - Implement the plan, execute the process, make the product.
Collect data for charting and analysis in the following "CHECK" and "ACT" steps.
CHECK - Study the actual results (measured and collected in "DO" above) and compare against the expected results (targets or goals from the "PLAN") to ascertain any differences Reference: CISA review manual 2014 page number 107
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle is a continuous improvement framework that helps organizations to achieve their objectives and improve their processes. It is a four-step iterative process that involves planning, implementing, monitoring, and adjusting activities to achieve desired results.
In the context of the question, the step of the PDCA cycle that requests corrective actions on significant differences between the actual versus the planned result is the "Act" step. The "Act" step involves taking corrective actions to address the significant differences between the actual and planned results.
The "Act" step includes the following activities:
Analyzing the results: In this step, the results of the previous steps are analyzed to identify significant differences between the actual and planned results.
Identifying the root cause: Once the significant differences are identified, the next step is to determine the root cause of the problem.
Developing a corrective action plan: Based on the analysis of the results and the identification of the root cause, a corrective action plan is developed to address the problem.
Implementing the corrective action plan: The corrective action plan is implemented to address the problem and improve the process.
Monitoring the results: The results of the corrective action plan are monitored to ensure that the problem has been addressed and the desired results have been achieved.
In summary, the "Act" step of the PDCA cycle is the step that requests corrective actions on significant differences between the actual versus the planned result. This step involves analyzing the results, identifying the root cause, developing a corrective action plan, implementing the plan, and monitoring the results to ensure that the problem has been addressed and the desired results have been achieved.
