Setting Up VPN Software on EC2 Instance
Question
You are setting up a VPN software on an EC2 Instance that will be used for VPN connections.
Which of the following is an important aspect that should be set on the EC2 Instance?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A.
Option B is incorrect since the source destination check on the Amazon EC2 instance should be disabled.
Option C is incorrect since this is required for Amazon provided VPN connections.
Option D is incorrect since this is not a primary requirement.
You have to Disable source destination check on the Amazon EC2 instance.
An example is also given in the AWS Documentation.
To launch an EC2 VPN instance.
1.Launch an Amazon Linux instance in a VPC public subnet and do the following:
a)Assign the VPN instance a static private IP address.
This is not required, but it makes setting up the config files easier.
In this example, use 10.0.0.5.
b)Allocate a VPC EIP and associate an EIP to your VPN instance.
In this example, use EIP1 to represent the public EIP address used to connect to your VPC.2
Disable Source/Dest checking on your EC2 instance.
a)Right-click the instance and selecting Change Source/Dest.
Check.
b)Click Yes, Disable.
For more an example on setting up a VPN software on an EC2 Instance, please refer to the below URL.
https://aws.amazon.com/articles/connecting-cisco-asa-to-vpc-ec2-instance-ipsec/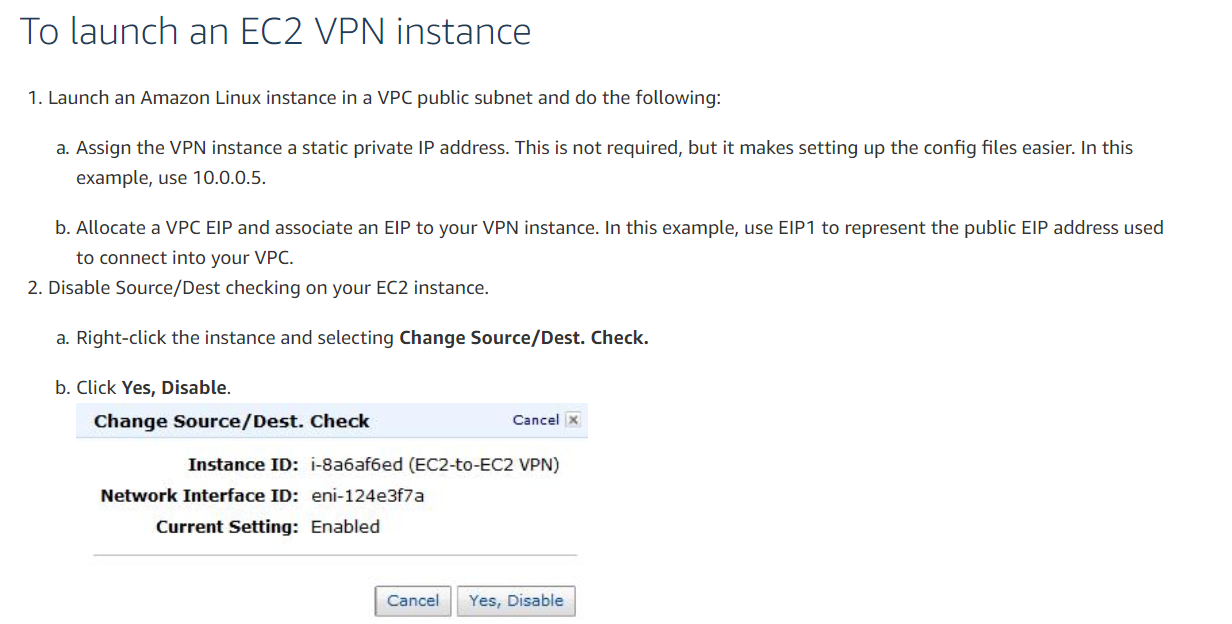
When setting up a VPN software on an EC2 instance for VPN connections, it's important to consider certain aspects to ensure the setup is secure and functional. One of the important aspects that should be set on the EC2 instance is to disable source/destination check.
Option A - Disable source destination check on the Amazon EC2 instance: This is the correct answer. By default, source/destination check is enabled on EC2 instances. It means that the instance performs network address translation (NAT) on the traffic passing through it. However, in the case of a VPN connection, the EC2 instance should pass the traffic to the virtual private gateway or customer gateway without performing any NAT. Therefore, it's important to disable source/destination check on the EC2 instance.
Option B - Enable source destination check on the Amazon EC2 instance: This option is not recommended for VPN connections as it will cause the EC2 instance to perform NAT on the traffic passing through it, which can interfere with the VPN connection.
Option C - Enable route propagation in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) subnet route table: This option is related to the routing of traffic in the VPC. While it's important to have the appropriate routing setup for the VPN connection, this option is not directly related to the EC2 instance setup.
Option D - Enable enhanced networking mode on the Amazon EC2 instance: This option is related to optimizing network performance for high-performance computing workloads. While it can be beneficial for some use cases, it's not directly related to the setup of a VPN software on an EC2 instance for VPN connections.
In summary, the correct answer is A, to disable source/destination check on the Amazon EC2 instance. This will ensure that the EC2 instance passes the traffic to the virtual private gateway or customer gateway without performing any NAT, which is necessary for a secure and functional VPN connection.
