Custom Error Page for Origin Server Issues
Question
A web application uses Amazon CloudFront to deliver its static and dynamic web content.
You want to customize the error page returned to the viewer when there is a problem with the origin server.
For example, if the origin server returns a 500 Internal Server Error, CloudFront should present a page that you have prepared.
How would you achieve this requirement in CloudFront?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Correct Answer - C.
Option A is incorrect because the custom error pages should be configured through CloudFront instead of the application.
Option B is incorrect because there is no need to create a new CloudFront distribution.
Option C is CORRECT because the error pages can be customized through CloudFront.
The following is an example.
Option D is incorrect because this is not how custom error responses are configured in CloudFront.
You cannot upload custom error pages to CloudFront directly.
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudFront/latest/DeveloperGuide/custom-error-pages.html.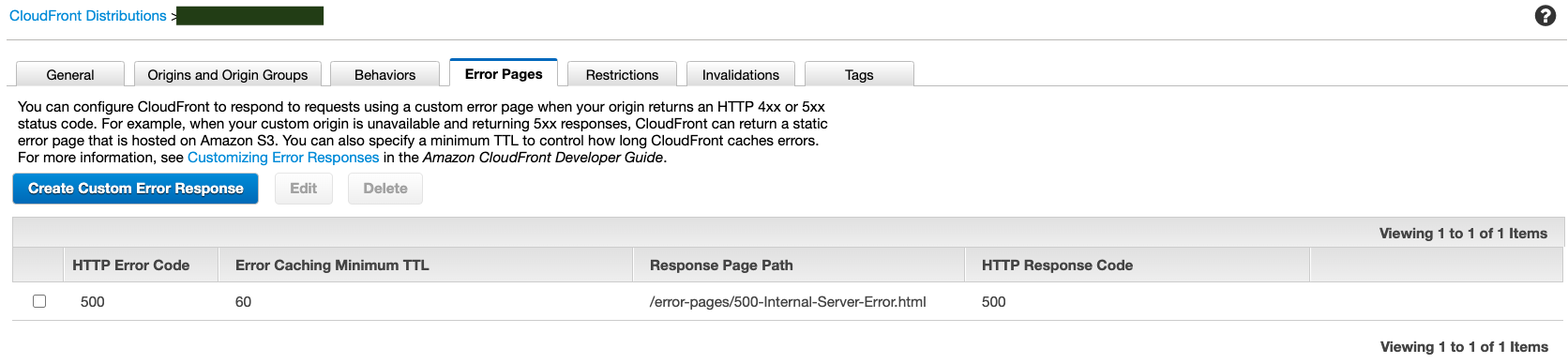
The correct answer is option C.
To customize error pages in Amazon CloudFront, you need to perform the following steps:
Store error pages in an S3 bucket: You need to upload your custom error pages to an S3 bucket. These error pages can be HTML, images, or any other static content.
Create a CloudFront distribution: After you have uploaded the error pages, you need to create a CloudFront distribution. In the distribution, you can specify the S3 bucket where your custom error pages are stored.
Configure custom error responses: In the CloudFront distribution, you can configure custom error responses for HTTP status codes 4xx and 5xx. For example, if there is a 404 Not Found error, CloudFront will present the custom error page you have specified for this error.
Verify your configuration: After you have configured custom error responses, you should verify your configuration by testing it. You can simulate an error by requesting a non-existent object from your CloudFront distribution. If everything is configured correctly, CloudFront should present the custom error page you have specified for the HTTP status code.
Option A is incorrect because modifying the application to store custom error pages will not work. The reason is that the application is responsible for serving content to CloudFront, and CloudFront cannot modify or replace the content that the origin server returns.
Option B is incorrect because creating a new CloudFront distribution is unnecessary. Instead, you can configure the existing CloudFront distribution to use the S3 bucket as the origin for custom error pages.
Option D is incorrect because uploading custom error pages to the CloudFront distribution will not work. The reason is that CloudFront is a content delivery network and does not allow you to modify or replace the content that the origin server returns.