Centralize and Encrypt Backups with AWS Backup
Question
Your team is planning to use AWS Backup to centralize the backup of various AWS and on-premises services.
The backups are required to be separated into different categories and saved in different containers.
Each container should have its own AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) key to encrypt backups.
How would you achieve this requirement?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Correct Answer: B.
Option A is incorrect because users cannot organize backups into S3 buckets.
AWS Backups use vaults to store the backups.
Option B is CORRECT because users should create several AWS Backup vaults and choose a different KMS key for each vault.
Please check the following snapshot on how to create a Backup vault:
Option C is incorrect because users cannot associate KMS keys with tags for AWS Backup.
This option is not applicable.
Option D is incorrect because users cannot associate a KMS key when configuring a backup plan.
References:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/vaults.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/aws-backup/latest/devguide/whatisbackup.html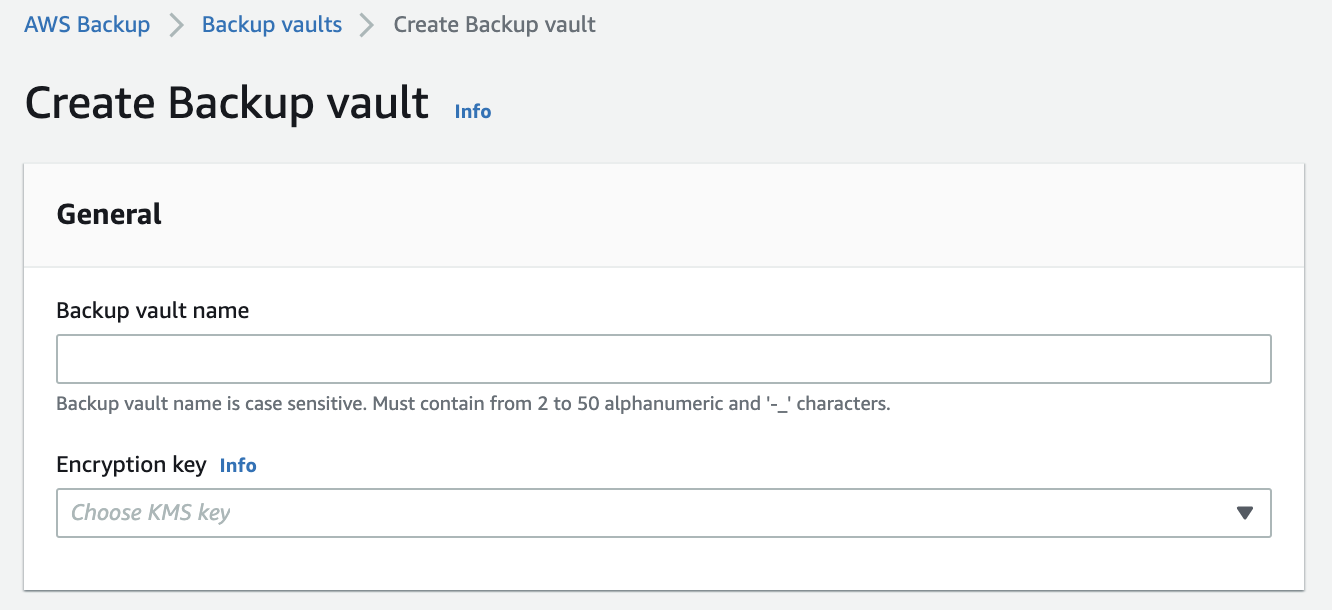
The correct answer is option B: Organize backups into different AWS Backup vaults with their own KMS keys.
Explanation: AWS Backup is a fully managed backup service that makes it easy to centralize and automate the backup of data across AWS services as well as on-premises environments. AWS Backup supports Amazon EBS volumes, Amazon RDS databases, Amazon DynamoDB tables, Amazon EFS file systems, AWS Storage Gateway volumes, and other AWS resources.
AWS Backup enables you to create backup plans that define the backup schedule, retention policy, and backup window for your backups. You can also specify the storage location for your backups, which can be an Amazon S3 bucket or an AWS Backup vault.
AWS Backup vault is a storage container where backups are stored. You can create multiple backup vaults in AWS Backup, and each backup vault can have its own set of permissions, lifecycle policies, and encryption settings.
To achieve the requirement of separating backups into different categories and saving them in different containers with their own KMS keys, the best approach is to organize backups into different AWS Backup vaults with their own KMS keys. This approach provides granular control over backups, allowing you to define different backup policies, retention periods, and encryption keys for each backup vault.
Organizing backups into different S3 buckets and enabling Server-Side Encryption with SSE-KMS (option A) provides encryption at rest for the backups, but it does not provide a way to organize backups into categories or to define different backup policies for different categories.
Organizing backups with different tags and associating a KMS key with each tag (option C) is not a valid approach since AWS Backup does not support tagging backups.
Organizing backups with different backup plans and configuring a dedicated KMS key for each backup plan (option D) is also not a valid approach since backup plans are designed to define backup schedules and retention policies, and they do not provide a way to organize backups into categories or to define different encryption keys for different categories.
