Deploying Containers for Microservices-Based Applications
Question
A start-up firm is developing a microservices-based application using open-source container orchestration.
This application will be integrated with other Public Cloud.
The firm does not have any expertise to provision & manage back-end infrastructure to set up this container.
You have been assigned to provide consultation for deploying containers. Which of the following will you suggest meeting the requirement?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Correct Answer: D.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service can be used to set up open-source Container orchestration like Kubernetes.
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service can be integrated with other public or private clouds.
AWS Fargate can be used as a serverless compute for deploying containers.
With AWS Fargate, there is no need to set back-end infrastructure for containers.
With AWS Fargate, based upon task definitions, containers are launched.
The following diagram depicts the deployment of AWS Kubernetes, with AWS Fargate, serverless containers can be deployed while using Amazon EC2, compute nodes are deployed manually as per requirement.
Using Amazon EC2 provides more control on back-end infrastructure for containers.
But customers have to perform management of these instances.
Option A is incorrect as with the Amazon EC2 launch type.
The firm will need to set up backend infrastructure & manage instance provisioning.
Option B & C are incorrect as the customer is looking for integration with Public Cloud & an open-source solution.
Amazon Elastic Container Service supports integration with AWS services & is an AWS Proprietary service.
For more information on AWS Fargate with Amazon EKS, refer to the following URLs-
https://aws.amazon.com/eks https://aws.amazon.com/fargate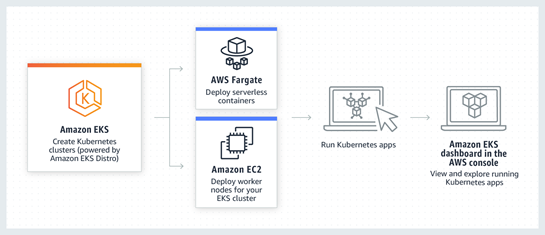
The requirement is to deploy containers for a microservices-based application that will be integrated with other public cloud, without the need for expertise to provision and manage backend infrastructure. In this scenario, the best option is to use a managed container service that provides ease of deployment, scaling, and management of containers.
Option A: Use Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service with Amazon EC2 launch type. Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a managed Kubernetes service that makes it easy to deploy, scale, and manage containerized applications using Kubernetes on AWS. With the Amazon EC2 launch type, you can use your own EC2 instances to run your EKS cluster's Kubernetes control plane instances and worker nodes. This option requires expertise in managing the EC2 instances, including monitoring, scaling, and patching.
Option B: Use Amazon Elastic Container Service with AWS Fargate launch type. Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is a fully-managed container orchestration service that makes it easy to run, stop, and manage Docker containers on a cluster. With the AWS Fargate launch type, you don't need to provision or manage any servers. AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers that eliminates the need to manage servers or clusters. This option provides the easiest way to deploy and manage containers without any backend infrastructure knowledge.
Option C: Use Amazon Elastic Container Service with Amazon EC2 launch type. This option is similar to Option B, except that you are responsible for provisioning, scaling, and managing the EC2 instances. This option requires expertise in managing the EC2 instances, including monitoring, scaling, and patching.
Option D: Use Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service with AWS Fargate launch type. This option combines the benefits of both Option A and Option B. You get the managed Kubernetes service with the ease of deployment provided by the AWS Fargate launch type. This option requires less expertise in managing the backend infrastructure compared to Option A.
In conclusion, the best option to meet the requirements of the scenario is Option B: Use Amazon Elastic Container Service with AWS Fargate launch type. This option provides a fully-managed container orchestration service with a serverless compute engine for containers, eliminating the need to provision or manage any servers or clusters.
