Question 45 of 48 from exam AZ-101: Microsoft Azure Integration and Security
Question
HOTSPOT -
Your company has offices in New York and Los Angeles.
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure virtual network named VNet1. Each office has a site-to-site VPN connection to VNet1.
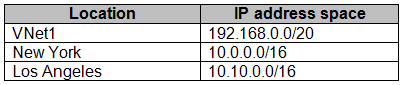
Each network uses the address spaces shown in the following table.
You need to ensure that all Internet-bound traffic from VNet1 is routed through the New York office.
What should you do? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
: Each correct selection is worth one point.
NOTE -
Hot Area:
Explanations
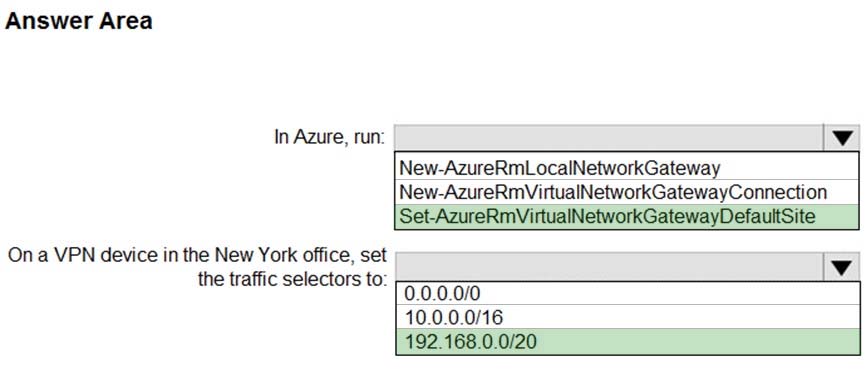
Box 1: Set-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayDefaultSite
The Set-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayDefaultSite cmdlet assigns a forced tunneling default site to a virtual network gateway. Forced tunneling provides a way for you to redirect Internet-bound traffic from Azure virtual machines to your on-premises network; this enables you to inspect and audit traffic before releasing it.
Forced tunneling is carried out by using a virtual private network (VPN) tunnel; this tunnel requires a default site, a local gateway where all the Azure Internet- bound traffic is redirected. Set-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayDefaultSite provides a way to change the default site assigned to a gateway.
Incorrect Answers:
Not: New-AzureRmVirtualNetworkGatewayConnection
This command creates the Site-to-Site VPN connection between the virtual network gateway and the on-prem VPN device. We already have Site-to-Site VPN connections.
Box 2: 192.168.0.0/20 -
Specify the VNET1 address.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/azurerm.network/set-azurermvirtualnetworkgatewaydefaultsite