Efficiently Managing Image Storage on AWS for Cost Optimization and Accessibility
Question
Your company recently launched a mobile application that allows users to take pictures of what they are eating daily, share with others, and get feedback to maintain a healthy diet routine.
These pictures are stored in S3 and served via the CloudFront.
The CEO of the company thinks the storage is not well optimized by looking at the bill.
He has asked to generate the access log reports and shift the images to different storage if they are not frequently used.
It is not very clear which images will be accessed frequently, but as per the past data analysis, the usage becomes low after the initial 3-4 weeks.
Please select the best option to optimize the cost and also maintain accessibility.
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D. E.Correct Answer: D.
Option A is INCORRECT because the CloudFront is used to deliver the images to end users to reduce the latency lag.
Edge Locations work as caching servers, and it saves the images based on the frequency of use.
However, CloudFront still loads the content from the origin S3 Bucket.
Option B is INCORRECT because migrating the images to Glacier will make it almost inaccessible after 3 weeks.
Glacier retrieval time is between 3-5 hours, and per the requirement, the application still needs to maintain accessibility.
Option C is INCORRECT because the CloudFront already geo-distributes the load and putting an elastic load balancer in front of it is not viable.
Option D is CORRECT because S3 Intelligent Tier automatically shifts content between Standard and Infrequent Access tier based on the usage pattern.
If the content is not used for 30 consecutive days, it will automatically be moved to the Infrequent Access tier.
Upon use, it will be transferred back to the Standard tier without any additional cost.
Option E is INCORRECT because serving images from EBS is not very scalable as compared to S3 storage.
There is no lifecycle event for EBS volumes.
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/s3/storage-classes/
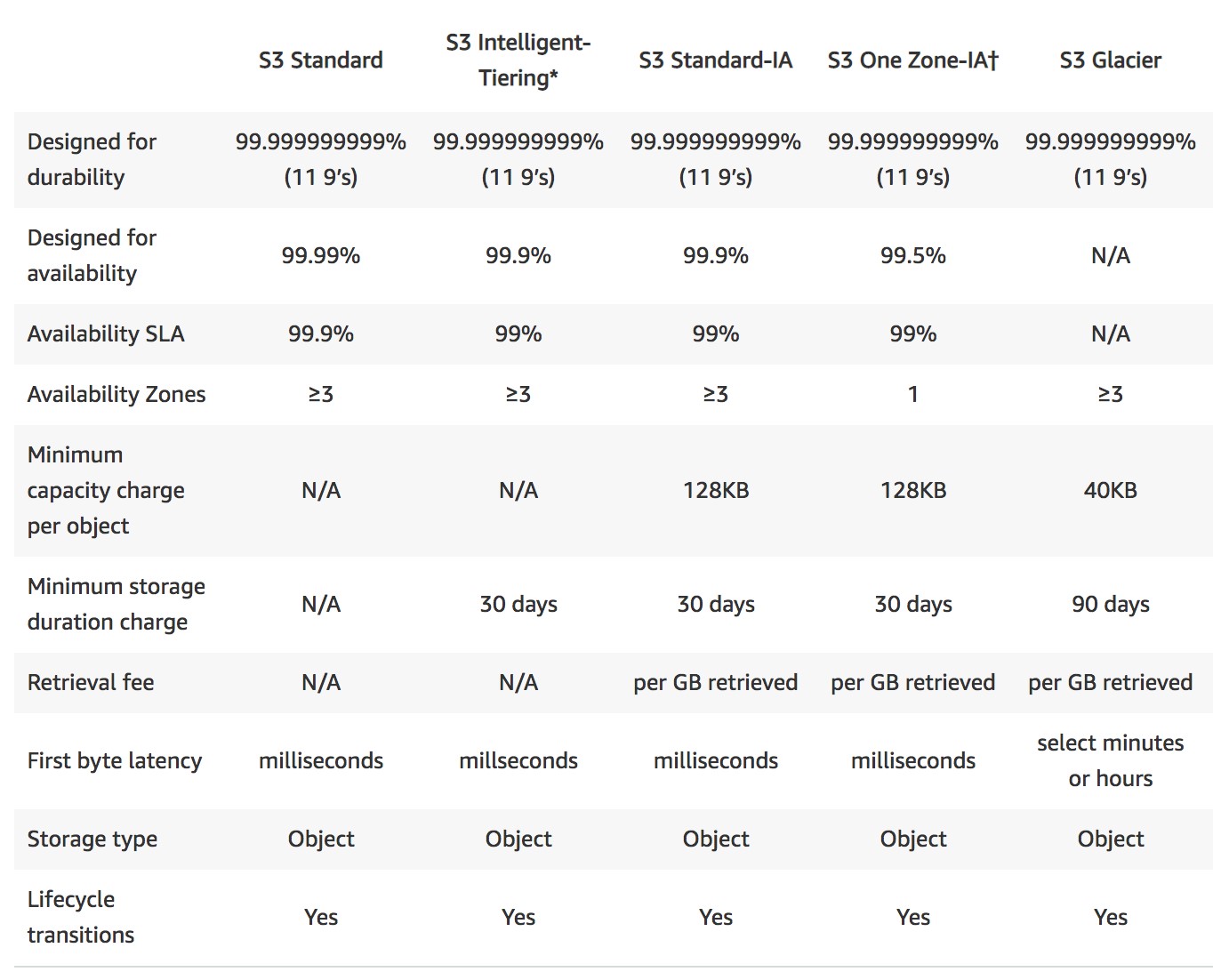
The best option to optimize the cost and maintain accessibility for the mobile application's images stored in S3 is to use S3 Intelligent Tiering. This storage class automatically moves objects between two access tiers, one for frequent access and another for infrequent access, based on changing access patterns. It is cost-effective and ensures that frequently accessed objects are readily available, while infrequently accessed objects are stored in a more cost-effective storage class.
Option A is incorrect because while CloudFront Edge Locations and access logs can optimize the storage cache based on the access pattern, it will not shift images to a different storage class as requested by the CEO. Additionally, it may not be clear which images will be accessed frequently and which will be infrequently accessed.
Option B is incorrect because Glacier is a long-term storage solution, and while it is cost-effective, it may not be optimal for images that users may want to access frequently.
Option C is also incorrect because it involves creating an elastic load balancer, which adds additional complexity and cost to the solution. It also requires setting up Kinesis to process logs, which adds additional setup and management overhead. This option may work in some cases, but it is not the best solution for this specific use case.
Option E is incorrect because it suggests storing the images on EC2 EBS, which is a block storage solution intended for use with EC2 instances. It would be more expensive to store the images on EC2 EBS, and it would require additional setup and management overhead. Moreover, it would not optimize the storage cost effectively as requested.
Therefore, the best option for optimizing the cost and maintaining accessibility of the images stored in S3 is to use S3 Intelligent Tiering, which automatically moves objects between two access tiers, based on changing access patterns, to provide cost-effective storage for the images.