Typical Use Cases of Amazon EFS One Zone Storage Classes
Question
Which of the following are typical use cases of Amazon EFS One Zone storage classes? (Select THREE)
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D. E.Answer: A, B, D.
The following table shows the characteristics of EFS vs.
EBS.
Refer to page 123 on the below link:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/efs-ug.pdf#performanceOption A, Option B, and Option D are characteristics of EFS.
Option C is characteristic of EBS.
Option E is characteristic of S3.
For more information on AWS EFS use cases, refer to the documentation here.
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/performance.html#performance-usecases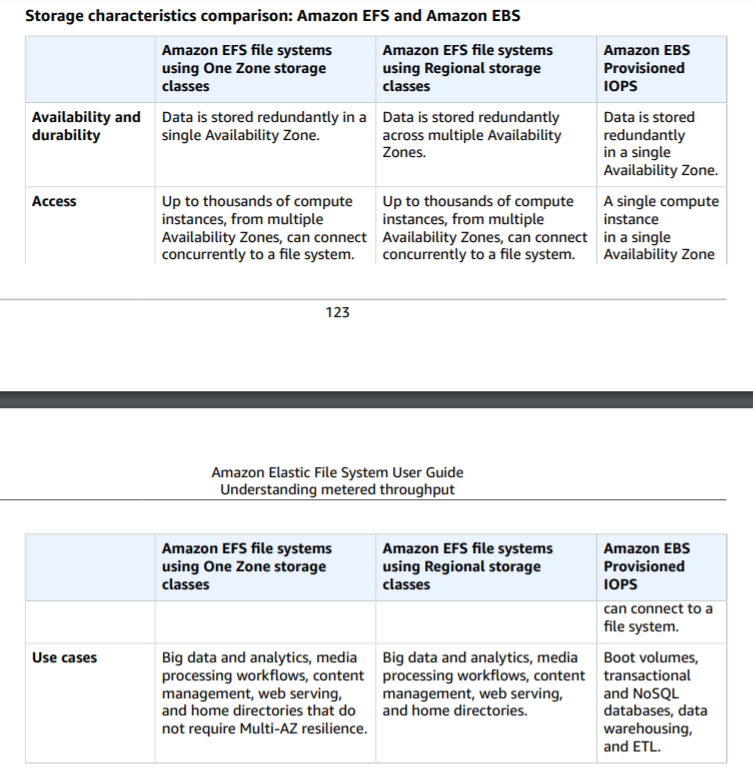
Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) is a fully managed file storage service for EC2 instances that provides scalable and highly available file storage for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources. EFS offers three storage classes: Standard, Infrequent Access (IA), and One Zone Infrequent Access (One Zone-IA). One Zone-IA is a lower-cost storage class compared to Standard and IA but provides a lower level of durability because data is stored in a single Availability Zone (AZ).
The typical use cases of Amazon EFS One Zone storage classes are:
A. Data is stored redundantly in a single AZ: One Zone-IA is designed for use cases where data is replaceable, such as content distribution, development and test, and transient data storage. It is not recommended for data that requires high levels of durability, such as mission-critical production workloads.
B. Up to thousands of Amazon EC2 instances from multiple AZs can connect concurrently to a file system: One Zone-IA can handle up to thousands of concurrent connections from multiple Amazon EC2 instances within the same VPC and AZ.
D. Big data and analytics, media processing workflows, content management, web serving, and home directories that do not require Multi-AZ resilience: One Zone-IA is suitable for workloads that do not require Multi-AZ resilience, such as big data and analytics, media processing workflows, content management, web serving, and home directories.
Therefore, the correct answers are A, B, and D. Option C is incorrect because One Zone-IA is not suitable for boot volumes, transactional and NoSQL databases, data warehousing, and ETL workloads that require high durability and Multi-AZ resilience. Option E is also incorrect because One Zone-IA does not support cross-region replication.