Applications Hosted by Service Providers: Exploring Cloud Computing Service Models | ISACA Exam
Question
In which of the following cloud computing service model are applications hosted by the service provider and made available to the customers over a network?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.A.
Software as a Service (Seas) is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the Internet.
Seas is closely related to the ASP (application service provider) and on demand computing software delivery models.
For your exam you should know below information about Cloud Computing: Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, three service models, and four deployment models.
Cloud computing service model - Cloud computing service models -
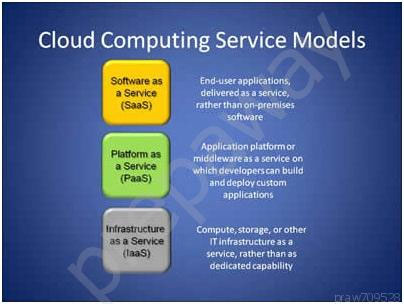
Software as a Service (Seas) Software as a Service (Seas) is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the Internet.
SaaS is closely related to the ASP (application service provider) and on demand computing software delivery models.
IDC identifies two slightly different delivery models for Seas.
The hosted application management (hosted AM) model is similar to ASP: a provider hosts commercially available software for customers and delivers it over the Web.
In the software on demand model, the provider gives customers network-based access to a single copy of an application created specifically for Seas distribution.
Provider gives users access to specific application software (CRM, e-mail, games)
The provider gives the customers network based access to a single copy of an application created specifically for Seas distribution and use.
Benefits of the Seas model include: easier administration automatic updates and patch management compatibility: All users will have the same version of software.
easier collaboration, for the same reason global accessibility.
Platform as a Service (Peas) Platform as a Service (Peas) is a way to rent hardware, operating systems, storage and network capacity over the Internet.
The service delivery model allows the customer to rent virtualized servers and associated services for running existing applications or developing and testing new ones.
Cloud providers deliver a computing platform, which can include an operating system, database, and web server as a holistic execution environment.
Where Iasi is the raw IT network, Peas is the software environment that runs on top of the IT network.
Platform as a Service (Peas) is an outgrowth of Software as a Service (Seas), a software distribution model in which hosted software applications are made available to customers over the Internet.
Peas has several advantages for developers.
With Peas, operating system features can be changed and upgraded frequently.
Geographically distributed development teams can work together on software development projects.
Services can be obtained from diverse sources that cross international boundaries.
Initial and ongoing costs can be reduced by the use of infrastructure services from a single vendor rather than maintaining multiple hardware facilities that often perform duplicate functions or suffer from incompatibility problems.
Overall expenses can also be minimized by unification of programming development efforts.
On the downside, Peas involves some risk of "lock-in" if offerings require proprietary service interfaces or development languages.
Another potential pitfall is that the flexibility of offerings may not meet the needs of some users whose requirements rapidly evolve.
Infrastructure as a Service (Iasi) Cloud providers offer the infrastructure environment of a traditional data center in an on-demand delivery method.
Companies deploy their own operating systems, applications, and software onto this provided infrastructure and are responsible for maintaining them.
Infrastructure as a Service is a provision model in which an organization outsources the equipment used to support operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components.
The service provider owns the equipment and is responsible for housing, running and maintaining it.
The client typically pays on a per-use basis.
The following answers are incorrect: Data as a service - Data Provided as a service rather than needing to be loaded and prepared on premises.
Platform as a service - Platform as a Service (Peas) is a way to rent hardware, operating systems, storage and network capacity over the Internet.
The service delivery model allows the customer to rent virtualized servers and associated services for running existing applications or developing and testing new ones.
Infrastructure as a service - Infrastructure as a Service is a provision model in which an organization outsources the equipment used to support operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components.
The service provider owns the equipment and is responsible for housing, running and maintaining it.
The client typically pays on a per-use basis.
http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Software-as-a-Service http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Platform-as-a-Service-PaaS http://searchcloudcomputing.techtarget.com/definition/Infrastructure-as-a-Service-IaaSThe cloud computing service model in which applications are hosted by the service provider and made available to the customers over a network is known as Software as a Service (SaaS).
In a SaaS model, the service provider hosts and maintains the application software and related infrastructure, which can be accessed by the customer over the internet. The customer typically accesses the software through a web browser, without the need to install and maintain the software on their own devices.
SaaS applications are generally designed to be highly scalable, reliable, and available to customers from any location, with minimal hardware or software requirements. Some common examples of SaaS applications include email, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
Data as a Service (DaaS) refers to a cloud computing service model where data is made available to customers over a network. DaaS providers typically offer data storage, processing, and analytics services to customers, allowing them to access and use data without the need for local infrastructure.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) refers to a cloud computing service model where the service provider offers a platform for customers to build, deploy, and manage their own applications, without the need to manage underlying infrastructure.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) refers to a cloud computing service model where the service provider offers virtualized infrastructure resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, which customers can use to build and deploy their own applications.
