Which Data Store to Choose for Ad-Hoc Queries and Table Joins?
Question
Your team has been tasked with the development of an application.
The backend store needs to store data on which ad-hoc queries can run, and table joins are required.
Which of the following would you use to host the underlying data store?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer - A.
The AWS Documentation gives an example comparison of when to use AWS RDS for SQL data and DynamoDB for NoSQL data.
Option B is incorrect because this should not be used when you have table joins to be carried out.
Option C is incorrect because this is used for object level storage.
Option D is incorrect because this is used for querying data in S3.
For more information on when to use SQL over NoSQL, please refer to the below URL-
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/SQLtoNoSQL.html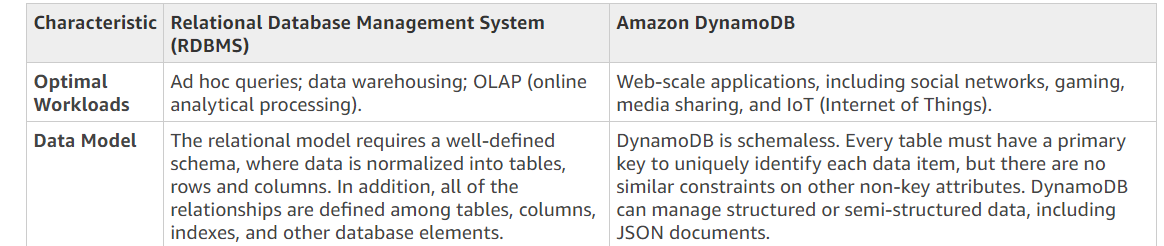
For an application that requires the storage of data on which ad-hoc queries can run and table joins are required, the best option would be a relational database.
AWS offers a number of database services, including RDS, DynamoDB, and Athena, but the best option would be AWS RDS.
AWS RDS (Relational Database Service) is a managed database service that makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. With RDS, you can choose from six popular database engines: Amazon Aurora, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and MariaDB. RDS supports both read replicas and Multi-AZ deployments for high availability and automatic failover.
DynamoDB is a NoSQL database, which means it is not well-suited for ad-hoc queries and table joins. While it is fast and scalable, it is designed for use cases that require low-latency access to small items of data.
S3 is an object storage service, not a database service. While S3 can store structured data, it is not optimized for running ad-hoc queries and table joins.
Athena is a query service that allows you to run ad-hoc queries against data stored in S3. While Athena is well-suited for ad-hoc queries, it is not optimized for table joins.
In summary, for an application that requires the storage of data on which ad-hoc queries can run and table joins are required, the best option would be AWS RDS.