Actions on an EBS Snapshot
Question
Which of the following is an action you cannot perform on an EBS snapshot?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: D.
Option A is a snapshot action.
Option B is a snapshot action.
Option C is a snapshot action.
Option D is the correct answer.
We can give permissions to snapshots based on AWS Account Numbers and not based on AWS Account names.
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ebs-modifying-snapshot-permissions.html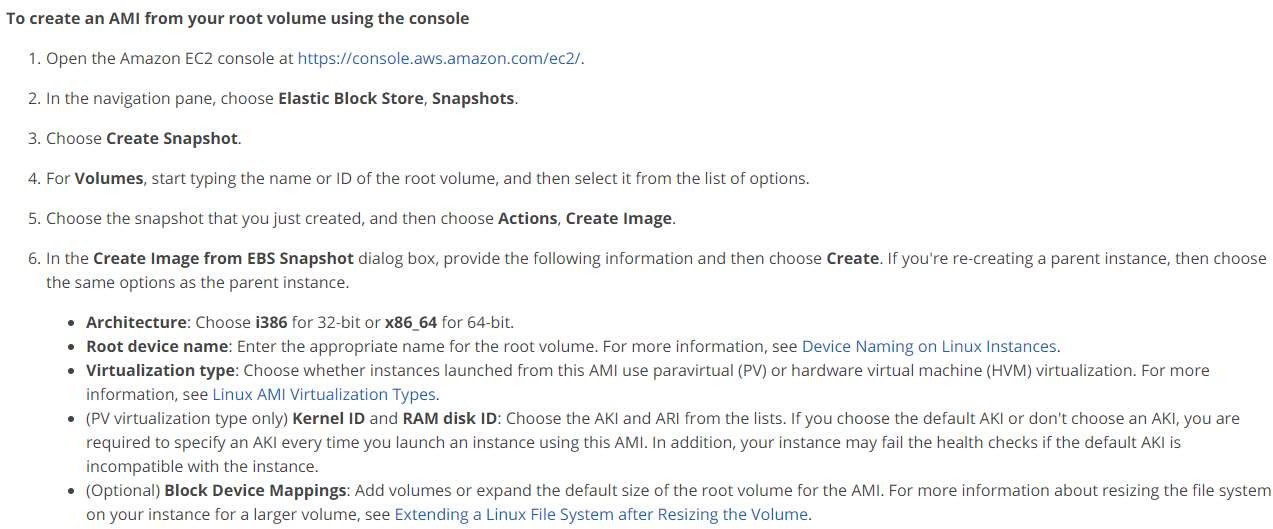
Answer: A. Create Image from snapshot.
Explanation:
EBS snapshots are point-in-time copies of an EBS volume. They can be used to create new EBS volumes or to restore an existing volume to a previous state. Snapshots are stored in Amazon S3 and can be used to migrate data between regions, copy data across accounts, and protect data for long-term retention.
The following actions can be performed on an EBS snapshot:
A. Create EBS volume from snapshot: You can create a new EBS volume from a snapshot. The new volume will be an exact copy of the original volume at the time the snapshot was taken.
B. Share a snapshot with another AWS account: You can share a snapshot with another AWS account. The other account will be able to create a new volume from the snapshot or use it to launch an EC2 instance.
C. Provide permissions to snapshots based on AWS Account Names: You can provide permissions to snapshots based on AWS Account Names. This allows you to control which AWS accounts can access the snapshot and what actions they can perform on it.
However, you cannot create an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) directly from an EBS snapshot. An AMI is a pre-configured virtual machine image, which includes the operating system, application server, and any additional software required to run the application. To create an AMI, you need to launch an EC2 instance from the snapshot and then create an image of the instance.
Therefore, the correct answer is A. Create Image from snapshot.
