Common Reasons for Failed Requests to an Application Load Balancer in AWS
Question
You have created a VPC with an application load balancer and selected two EC2 instances as targets.
However, when you are trying to make a request to the internet-facing load balancer, the request fails.
What could be the reason?
Answers
Explanations
Click on the arrows to vote for the correct answer
A. B. C. D.Answer: A.
Option A is correct because there must be a route in a route table to the internet gateway for internet connectivity
Option B is incorrect because this does not result in the failure mentioned in the question.
Option C is incorrect because any instances in the VPC must either have a public IP address or an attached Elastic IP address.
And for the internet-facing load balancer, AWS manages the underlying IP addresses.
So no need for an Elastic IP address.
Option D is incorrect because cross-zone load balancing is not a reason to cause the failure.
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/create-attach-igw-vpc/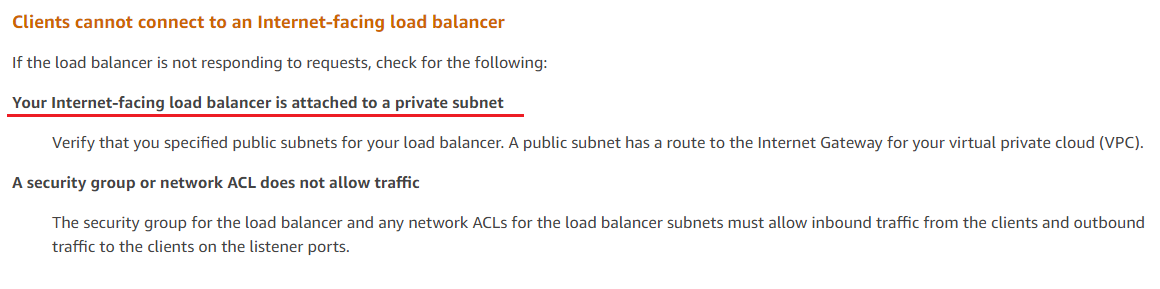
The most likely reason for the request to fail when accessing the internet-facing application load balancer (ALB) is that the associated subnet's route table does not have a route to the internet gateway.
A route to the internet gateway is necessary for internet traffic to reach the EC2 instances through the ALB. Therefore, to resolve this issue, you should add a route to the subnet's route table that points to the internet gateway.
Option B (Target EC2 instances are in a public subnet) is not a reason for the request to fail because instances in a public subnet can be accessed from the internet.
Option C (No Elastic IP address attached to the load balancer) is not a requirement for an ALB. However, if you need to provide a static IP address for the ALB, then you can associate an Elastic IP address with it.
Option D (Cross-zone load balancing is not enabled) affects the distribution of traffic across the target instances within the same Availability Zone. However, it is not a cause of the request to fail.